Product Description
ROLLER CHAIN
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CHAIN
Two different sizes of roller chain, showing construction.
There are 2 types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having 2 inner plates held together by 2 sleeves or bushings CHINAMFG which rotate 2 rollers. Inner links alternate with the second type, the outer links, consisting of 2 outer plates held together by pins passing through the bushings of the inner links. The “bushingless” roller chain is similar in operation though not in construction; instead of separate bushings or sleeves holding the inner plates together, the plate has a tube stamped into it protruding from the hole which serves the same purpose. This has the advantage of removing 1 step in assembly of the chain.
The roller chain design reduces friction compared to simpler designs, resulting in higher efficiency and less wear. The original power transmission chain varieties lacked rollers and bushings, with both the inner and outer plates held by pins which directly contacted the sprocket teeth; however this configuration exhibited extremely rapid wear of both the sprocket teeth, and the plates where they pivoted on the pins. This problem was partially solved by the development of bushed chains, with the pins holding the outer plates passing through bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This distributed the wear over a greater area; however the teeth of the sprockets still wore more rapidly than is desirable, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and provided rolling contact with the teeth of the sprockets resulting in excellent resistance to wear of both sprockets and chain as well. There is even very low friction, as long as the chain is sufficiently lubricated. Continuous, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of primary importance for efficient operation as well as correct tensioning.
LUBRICATION
Many driving chains (for example, in factory equipment, or driving a camshaft inside an internal combustion engine) operate in clean environments, and thus the wearing surfaces (that is, the pins and bushings) are safe from precipitation and airborne grit, many even in a sealed environment such as an oil bath. Some roller chains are designed to have o-rings built into the space between the outside link plate and the inside roller link plates. Chain manufacturers began to include this feature in 1971 after the application was invented by Joseph Montano while working for Whitney Chain of Hartford, Connecticut. O-rings were included as a way to improve lubrication to the links of power transmission chains, a service that is vitally important to extending their working life. These rubber fixtures form a barrier that holds factory applied lubricating grease inside the pin and bushing wear areas. Further, the rubber o-rings prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering inside the chain linkages, where such particles would otherwise cause significant wear.[citation needed]
There are also many chains that have to operate in dirty conditions, and for size or operational reasons cannot be sealed. Examples include chains on farm equipment, bicycles, and chain saws. These chains will necessarily have relatively high rates of wear, particularly when the operators are prepared to accept more friction, less efficiency, more noise and more frequent replacement as they neglect lubrication and adjustment.
Many oil-based lubricants attract dirt and other particles, eventually forming an CHINAMFG paste that will compound wear on chains. This problem can be circumvented by use of a “dry” PTFE spray, which forms a solid film after application and repels both particles and moisture.
VARIANTS DESIGN
Layout of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Inner plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller
If the chain is not being used for a high wear application (for instance if it is just transmitting motion from a hand-operated lever to a control shaft on a machine, or a sliding door on an oven), then 1 of the simpler types of chain may still be used. Conversely, where extra strength but the smooth drive of a smaller pitch is required, the chain may be “siamesed”; instead of just 2 rows of plates on the outer sides of the chain, there may be 3 (“duplex”), 4 (“triplex”), or more rows of plates running parallel, with bushings and rollers between each adjacent pair, and the same number of rows of teeth running in parallel on the sprockets to match. Timing chains on automotive engines, for example, typically have multiple rows of plates called strands.
Roller chain is made in several sizes, the most common American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards being 40, 50, 60, and 80. The first digit(s) indicate the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the last digit being 0 for standard chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. Thus, a chain with half-inch pitch would be a #40 while a #160 sprocket would have teeth spaced 2 inches apart, etc. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch; thus a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but stainless steel is used in food processing machinery or other places where lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are occasionally seen for the same reason.
Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up using a master link (also known as a connecting link), which typically has 1 pin held by a horseshoe clip rather than friction fit, allowing it to be inserted or removed with simple tools. Chain with a removable link or pin is also known as cottered chain, which allows the length of the chain to be adjusted. Half links (also known as offsets) are available and are used to increase the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the master link (also known as a connecting link) “riveted” or mashed on the ends. These pins are made to be durable and are not removable.
USE
An example of 2 ‘ghost’ sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain system
Roller chains are used in low- to mid-speed drives at around 600 to 800 feet per minute; however, at higher speeds, around 2,000 to 3,000 feet per minute, V-belts are normally used due to wear and noise issues.
A bicycle chain is a form of roller chain. Bicycle chains may have a master link, or may require a chain tool for removal and installation. A similar but larger and thus stronger chain is used on most motorcycles although it is sometimes replaced by either a toothed belt or a shaft drive, which offer lower noise level and fewer maintenance requirements.
The great majority of automobile engines use roller chains to drive the camshaft(s). Very high performance engines often use gear drive, and starting in the early 1960s toothed belts were used by some manufacturers.
Chains are also used in forklifts using hydraulic rams as a pulley to raise and lower the carriage; however, these chains are not considered roller chains, but are classified as lift or leaf chains.
Chainsaw cutting chains superficially resemble roller chains but are more closely related to leaf chains. They are driven by projecting drive links which also serve to locate the chain CHINAMFG the bar.
Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 front (cold) vector thrust nozzle – the nozzle is rotated by a chain drive from an air motor
A perhaps unusual use of a pair of motorcycle chains is in the Harrier Jump Jet, where a chain drive from an air motor is used to rotate the movable engine nozzles, allowing them to be pointed downwards for hovering flight, or to the rear for normal CHINAMFG flight, a system known as Thrust vectoring.
WEAR
The effect of wear on a roller chain is to increase the pitch (spacing of the links), causing the chain to grow longer. Note that this is due to wear at the pivoting pins and bushes, not from actual stretching of the metal (as does happen to some flexible steel components such as the hand-brake cable of a motor vehicle).
With modern chains it is unusual for a chain (other than that of a bicycle) to wear until it breaks, since a worn chain leads to the rapid onset of wear on the teeth of the sprockets, with ultimate failure being the loss of all the teeth on the sprocket. The sprockets (in particular the smaller of the two) suffer a grinding motion that puts a characteristic hook shape into the driven face of the teeth. (This effect is made worse by a chain improperly tensioned, but is unavoidable no matter what care is taken). The worn teeth (and chain) no longer provides smooth transmission of power and this may become evident from the noise, the vibration or (in car engines using a timing chain) the variation in ignition timing seen with a timing light. Both sprockets and chain should be replaced in these cases, since a new chain on worn sprockets will not last long. However, in less severe cases it may be possible to save the larger of the 2 sprockets, since it is always the smaller 1 that suffers the most wear. Only in very light-weight applications such as a bicycle, or in extreme cases of improper tension, will the chain normally jump off the sprockets.
The lengthening due to wear of a chain is calculated by the following formula:
M = the length of a number of links measured
S = the number of links measured
P = Pitch
In industry, it is usual to monitor the movement of the chain tensioner (whether manual or automatic) or the exact length of a drive chain (one rule of thumb is to replace a roller chain which has elongated 3% on an adjustable drive or 1.5% on a fixed-center drive). A simpler method, particularly suitable for the cycle or motorcycle user, is to attempt to pull the chain away from the larger of the 2 sprockets, whilst ensuring the chain is taut. Any significant movement (e.g. making it possible to see through a gap) probably indicates a chain worn up to and beyond the limit. Sprocket damage will result if the problem is ignored. Sprocket wear cancels this effect, and may mask chain wear.
CHAIN STRENGTH
The most common measure of roller chain’s strength is tensile strength. Tensile strength represents how much load a chain can withstand under a one-time load before breaking. Just as important as tensile strength is a chain’s fatigue strength. The critical factors in a chain’s fatigue strength is the quality of steel used to manufacture the chain, the heat treatment of the chain components, the quality of the pitch hole fabrication of the linkplates, and the type of shot plus the intensity of shot peen coverage on the linkplates. Other factors can include the thickness of the linkplates and the design (contour) of the linkplates. The rule of thumb for roller chain operating on a continuous drive is for the chain load to not exceed a mere 1/6 or 1/9 of the chain’s tensile strength, depending on the type of master links used (press-fit vs. slip-fit)[citation needed]. Roller chains operating on a continuous drive beyond these thresholds can and typically do fail prematurely via linkplate fatigue failure.
The standard minimum ultimate strength of the ANSI 29.1 steel chain is 12,500 x (pitch, in inches)2. X-ring and O-Ring chains greatly decrease wear by means of internal lubricants, increasing chain life. The internal lubrication is inserted by means of a vacuum when riveting the chain together.
CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An “H” following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, “10 speed chain”. Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2″ x 1/8″ chains, where 1/8″ refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CHINAMFG Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CHINAMFG range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Food Machinery, Marine, Mining Equipment, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Welding, Loading, Forging |
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Structure: | Roller Chain |
| Material: | Alloy |
| Type: | Bush Chain |
| Samples: |
US$ 4/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|


Are there any smart or automated car parking chain solutions that offer advanced features for improved efficiency?
Yes, there are smart and automated car parking chain solutions available that offer advanced features to enhance efficiency and user experience. These technologies leverage automation, data analytics, and connectivity to provide various benefits:
1. Automated Access Control: Smart parking chains are integrated with electronic access control systems, allowing for automatic detection of authorized vehicles and seamless entry without the need for manual intervention.
2. License Plate Recognition (LPR): Some automated systems use LPR technology to identify vehicles by their license plates, granting access to pre-registered vehicles without the need for physical credentials.
3. Mobile Apps: Smart parking chain solutions may have companion mobile apps that enable users to request access, pay for parking, or receive notifications about parking availability and status.
4. Reservation Systems: Advanced parking chains can be integrated with reservation systems, allowing users to reserve parking spaces in advance, ensuring a spot is available upon arrival.
5. Real-time Data: Smart parking chains can collect and provide real-time data on parking occupancy, traffic patterns, and usage, helping facility managers optimize parking space allocation and make informed decisions.
6. Remote Management: Automated parking chains can be remotely controlled, allowing operators to manage access and monitor the parking facility from a central location.
7. Intelligent Traffic Flow: Some smart systems can analyze traffic flow and optimize entry and exit points to reduce congestion and waiting times.
8. Payment Integration: Smart parking chains can be linked to payment systems, enabling automatic payment processing for users with valid access rights.
9. Integration with Other Technologies: Smart parking chains can be integrated with other technologies, such as parking guidance systems or smart sensors, to create a comprehensive and efficient parking management solution.
10. Enhanced Security: With automated access control and data monitoring, smart parking chain solutions offer enhanced security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and enhancing user safety.
These advanced features make smart and automated car parking chains an attractive choice for modern parking facilities, offering improved efficiency, convenience, and user satisfaction.

What are the maintenance requirements for car parking chains to ensure smooth operation over time?
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the smooth operation and longevity of car parking chains. Proper care and attention will help prevent malfunctions and ensure reliable access control in parking facilities. Here are the key maintenance requirements:
1. Cleaning: Regularly clean the parking chains to remove dirt, dust, and debris that can accumulate over time. Clean chains ensure smooth movement and prevent unnecessary wear.
2. Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubrication to the chain links and any moving parts of the chain mechanism. Lubrication reduces friction and wear, allowing the chain to move smoothly.
3. Inspection: Conduct routine inspections of the parking chains to identify any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Promptly address any issues to prevent further damage and ensure optimal performance.
4. Adjustments: Check the tension and alignment of the chains regularly. Make necessary adjustments to ensure the chain remains properly tensioned and aligned.
5. Replacement of Worn Parts: If any components of the parking chain show significant wear or damage, replace them promptly to maintain the chain’s integrity and functionality.
6. Weather Protection: Apply protective coatings or paint to steel chains to minimize the impact of weather elements and reduce the risk of corrosion.
7. Addressing Corrosion: For chains made of materials susceptible to corrosion, such as steel, regularly inspect for signs of rust and treat affected areas to prevent further corrosion.
8. Preventing Obstructions: Ensure that the area around the parking chains is clear of any obstacles that could hinder their movement or cause damage.
9. Training and Education: Train parking attendants or personnel responsible for operating the parking chains to handle them properly and conduct basic maintenance tasks.
10. Regular Testing: Periodically test the raising and lowering mechanism of the parking chains to verify that they are functioning correctly.
By adhering to these maintenance requirements, parking facility managers can ensure the smooth operation and reliability of car parking chains, minimizing downtime and ensuring efficient access control for vehicles in the long run.

What are the benefits of using a car parking chain compared to other parking control methods?
Car parking chains offer several advantages over other parking control methods:
- Cost-effectiveness: Parking chains are generally more affordable to install and maintain compared to more complex systems like automated gates or barrier arms.
- Simplicity: They provide a straightforward and easy-to-understand method for controlling vehicle access, requiring minimal training for attendants or personnel.
- Durability: Made from sturdy metal materials, parking chains are robust and can withstand various weather conditions and potential wear and tear.
- Flexibility: Parking chains can be used in various locations, including small parking lots, private driveways, or temporary event spaces, where a permanent gate system may not be feasible.
- Manual and Automated Options: Depending on the setup, parking chains can be operated manually by attendants or automated using electronic access control systems, offering convenience for users.
- Visual Deterrent: The presence of a chain across the entrance acts as a visual deterrent, dissuading unauthorized vehicles from attempting to enter the parking area.
While car parking chains are advantageous in many situations, they may not be suitable for high-traffic areas or locations where more sophisticated access control is necessary for security reasons. In such cases, other methods like automated gates, barrier arms, or ticket-based systems may be more appropriate.
“`

editor by CX 2023-11-20
China wholesaler Martin Gearbox Short-Pitch 36A-2 Precision Industrial Machinery Roller Chains for Car Parking and Excavator
Product Description
Basic Info
|
ANSI NO: |
180-2R |
DIN/ISO NO: |
36A-2 |
|
Pitch (mm): |
57.1500 |
Roller Diameter(mm): |
35.71 |
|
Inner Plate Width (mm): |
35.48 |
Average Tensile Strength: |
722.2KN |
|
Pin Diameter(mm): |
17.46 |
Plate Thickness (mm): |
7.20 |
|
Weight / Meter (kgs/m): |
13.45 |
Chain Size: |
5F, 10F, 5Meters |
|
Origin: |
HangZhou China |
HS Code: |
7315119000 |
1. Providing 10 series more than 8000 models of chains,Heavy duty engineering chains, oil field chains, heavy duty port crane chains, metallurgy conveyor chains, ultra-high tension escalator chains, mining chains, etc, and customized solutions.
2. More than 80% of our roller chain are exported to all over the world, We are serving customers of top 5 of world famous manufacturers , and more than 90% of our turnover are from the cooperation with the manufacturers in the world.
3. Having advanced online inspection for automatic assembly lines.
4. Having nation level Enterprise Technology Center, we cost no less than 13% of our annual turnover investment in R&D each year.
5. Having our own Standardization Management Committee in our company, and participated in the formulation and modification of the roller chain standards of the People’s Republic of China.
SMCC roller chain is 1 of the most widely used and welcome products in the market. Its continuous innovative development is suitable to be the solutions for many conditions, standard roller chains, motorcycle driving chain, O-ring motorcycle chain, high strength roller chain, conveyor chains, agricultural driving chain, galvanized chain, nickel-plated chain, lubrication-free chain and oilfield chain etc
Our CHINAMFG chain was produced by machinery processing from raw materials to finished products and a full set of quality testing equipment. Mechanical processing equipment include grinding machines, high speed punching machines, milling machines, high speed automatic rolling and assembling machine. Heat treatment was processed by continuous mesh belt conveyor furnace, mesh belt conveyor annealing furnace, advanced central control system of heat treatment, rotary CHINAMFG for chain component heat treatment, which ensure the stability and consistency of the key function of chain components.
We are the best suppliers of Chinese largest palletizing robot enterprises. These items are durable quality with affordable prices, replace of Japan chains, ZheJiang chains exported to Europe, America, Asia and other countries and regions.
Workshop Show
ROLLER CHAIN
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CHAIN
Two different sizes of roller chain, showing construction.
There are 2 types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having 2 inner plates held together by 2 sleeves or bushings CHINAMFG which rotate 2 rollers. Inner links alternate with the second type, the outer links, consisting of 2 outer plates held together by pins passing through the bushings of the inner links. The “bushingless” roller chain is similar in operation though not in construction; instead of separate bushings or sleeves holding the inner plates together, the plate has a tube stamped into it protruding from the hole which serves the same purpose. This has the advantage of removing 1 step in assembly of the chain.
The roller chain design reduces friction compared to simpler designs, resulting in higher efficiency and less wear. The original power transmission chain varieties lacked rollers and bushings, with both the inner and outer plates held by pins which directly contacted the sprocket teeth; however this configuration exhibited extremely rapid wear of both the sprocket teeth, and the plates where they pivoted on the pins. This problem was partially solved by the development of bushed chains, with the pins holding the outer plates passing through bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This distributed the wear over a greater area; however the teeth of the sprockets still wore more rapidly than is desirable, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and provided rolling contact with the teeth of the sprockets resulting in excellent resistance to wear of both sprockets and chain as well. There is even very low friction, as long as the chain is sufficiently lubricated. Continuous, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of primary importance for efficient operation as well as correct tensioning.
LUBRICATION
Many driving chains (for example, in factory equipment, or driving a camshaft inside an internal combustion engine) operate in clean environments, and thus the wearing surfaces (that is, the pins and bushings) are safe from precipitation and airborne grit, many even in a sealed environment such as an oil bath. Some roller chains are designed to have o-rings built into the space between the outside link plate and the inside roller link plates. Chain manufacturers began to include this feature in 1971 after the application was invented by Joseph Montano while working for Whitney Chain of Hartford, Connecticut. O-rings were included as a way to improve lubrication to the links of power transmission chains, a service that is vitally important to extending their working life. These rubber fixtures form a barrier that holds factory applied lubricating grease inside the pin and bushing wear areas. Further, the rubber o-rings prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering inside the chain linkages, where such particles would otherwise cause significant wear.[citation needed]
There are also many chains that have to operate in dirty conditions, and for size or operational reasons cannot be sealed. Examples include chains on farm equipment, bicycles, and chain saws. These chains will necessarily have relatively high rates of wear, particularly when the operators are prepared to accept more friction, less efficiency, more noise and more frequent replacement as they neglect lubrication and adjustment.
Many oil-based lubricants attract dirt and other particles, eventually forming an CHINAMFG paste that will compound wear on chains. This problem can be circumvented by use of a “dry” PTFE spray, which forms a solid film after application and repels both particles and moisture.
VARIANTS DESIGN
Layout of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Inner plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller
If the chain is not being used for a high wear application (for instance if it is just transmitting motion from a hand-operated lever to a control shaft on a machine, or a sliding door on an oven), then 1 of the simpler types of chain may still be used. Conversely, where extra strength but the smooth drive of a smaller pitch is required, the chain may be “siamesed”; instead of just 2 rows of plates on the outer sides of the chain, there may be 3 (“duplex”), 4 (“triplex”), or more rows of plates running parallel, with bushings and rollers between each adjacent pair, and the same number of rows of teeth running in parallel on the sprockets to match. Timing chains on automotive engines, for example, typically have multiple rows of plates called strands.
Roller chain is made in several sizes, the most common American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards being 40, 50, 60, and 80. The first digit(s) indicate the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the last digit being 0 for standard chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. Thus, a chain with half-inch pitch would be a #40 while a #160 sprocket would have teeth spaced 2 inches apart, etc. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch; thus a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but stainless steel is used in food processing machinery or other places where lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are occasionally seen for the same reason.
Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up using a master link (also known as a connecting link), which typically has 1 pin held by a horseshoe clip rather than friction fit, allowing it to be inserted or removed with simple tools. Chain with a removable link or pin is also known as cottered chain, which allows the length of the chain to be adjusted. Half links (also known as offsets) are available and are used to increase the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the master link (also known as a connecting link) “riveted” or mashed on the ends. These pins are made to be durable and are not removable.
USE
An example of 2 ‘ghost’ sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain system
Roller chains are used in low- to mid-speed drives at around 600 to 800 feet per minute; however, at higher speeds, around 2,000 to 3,000 feet per minute, V-belts are normally used due to wear and noise issues.
A bicycle chain is a form of roller chain. Bicycle chains may have a master link, or may require a chain tool for removal and installation. A similar but larger and thus stronger chain is used on most motorcycles although it is sometimes replaced by either a toothed belt or a shaft drive, which offer lower noise level and fewer maintenance requirements.
The great majority of automobile engines use roller chains to drive the camshaft(s). Very high performance engines often use gear drive, and starting in the early 1960s toothed belts were used by some manufacturers.
Chains are also used in forklifts using hydraulic rams as a pulley to raise and lower the carriage; however, these chains are not considered roller chains, but are classified as lift or leaf chains.
Chainsaw cutting chains superficially resemble roller chains but are more closely related to leaf chains. They are driven by projecting drive links which also serve to locate the chain CHINAMFG the bar.
Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 front (cold) vector thrust nozzle – the nozzle is rotated by a chain drive from an air motor
A perhaps unusual use of a pair of motorcycle chains is in the Harrier Jump Jet, where a chain drive from an air motor is used to rotate the movable engine nozzles, allowing them to be pointed downwards for hovering flight, or to the rear for normal CHINAMFG flight, a system known as Thrust vectoring.
WEAR
The effect of wear on a roller chain is to increase the pitch (spacing of the links), causing the chain to grow longer. Note that this is due to wear at the pivoting pins and bushes, not from actual stretching of the metal (as does happen to some flexible steel components such as the hand-brake cable of a motor vehicle).
With modern chains it is unusual for a chain (other than that of a bicycle) to wear until it breaks, since a worn chain leads to the rapid onset of wear on the teeth of the sprockets, with ultimate failure being the loss of all the teeth on the sprocket. The sprockets (in particular the smaller of the two) suffer a grinding motion that puts a characteristic hook shape into the driven face of the teeth. (This effect is made worse by a chain improperly tensioned, but is unavoidable no matter what care is taken). The worn teeth (and chain) no longer provides smooth transmission of power and this may become evident from the noise, the vibration or (in car engines using a timing chain) the variation in ignition timing seen with a timing light. Both sprockets and chain should be replaced in these cases, since a new chain on worn sprockets will not last long. However, in less severe cases it may be possible to save the larger of the 2 sprockets, since it is always the smaller 1 that suffers the most wear. Only in very light-weight applications such as a bicycle, or in extreme cases of improper tension, will the chain normally jump off the sprockets.
The lengthening due to wear of a chain is calculated by the following formula:
M = the length of a number of links measured
S = the number of links measured
P = Pitch
In industry, it is usual to monitor the movement of the chain tensioner (whether manual or automatic) or the exact length of a drive chain (one rule of thumb is to replace a roller chain which has elongated 3% on an adjustable drive or 1.5% on a fixed-center drive). A simpler method, particularly suitable for the cycle or motorcycle user, is to attempt to pull the chain away from the larger of the 2 sprockets, whilst ensuring the chain is taut. Any significant movement (e.g. making it possible to see through a gap) probably indicates a chain worn up to and beyond the limit. Sprocket damage will result if the problem is ignored. Sprocket wear cancels this effect, and may mask chain wear.
CHAIN STRENGTH
The most common measure of roller chain’s strength is tensile strength. Tensile strength represents how much load a chain can withstand under a one-time load before breaking. Just as important as tensile strength is a chain’s fatigue strength. The critical factors in a chain’s fatigue strength is the quality of steel used to manufacture the chain, the heat treatment of the chain components, the quality of the pitch hole fabrication of the linkplates, and the type of shot plus the intensity of shot peen coverage on the linkplates. Other factors can include the thickness of the linkplates and the design (contour) of the linkplates. The rule of thumb for roller chain operating on a continuous drive is for the chain load to not exceed a mere 1/6 or 1/9 of the chain’s tensile strength, depending on the type of master links used (press-fit vs. slip-fit)[citation needed]. Roller chains operating on a continuous drive beyond these thresholds can and typically do fail prematurely via linkplate fatigue failure.
The standard minimum ultimate strength of the ANSI 29.1 steel chain is 12,500 x (pitch, in inches)2. X-ring and O-Ring chains greatly decrease wear by means of internal lubricants, increasing chain life. The internal lubrication is inserted by means of a vacuum when riveting the chain together.
CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An “H” following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, “10 speed chain”. Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2″ x 1/8″ chains, where 1/8″ refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CHINAMFG Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CHINAMFG range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
| Production Scope: | Parts Production Line |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Automation: | Automation |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|


Can car parking chains be retrofitted into existing parking facilities to upgrade their security measures?
Yes, car parking chains can be retrofitted into existing parking facilities to upgrade their security measures and access control. Retrofitting parking chains is a practical and cost-effective solution for improving security without the need for major infrastructure changes. Here’s how it can be done:
1. Site Assessment: Conduct a thorough site assessment to identify suitable locations for installing the parking chains. Consider factors such as traffic flow, vehicle types, and entry/exit points.
2. Choose the Right Chains: Select parking chains that are compatible with the existing facility and meet the security requirements. Consider factors like traffic volume, weather resistance, and automation options.
3. Anchor Points: Identify and prepare sturdy anchor points on either side of the entrance or exit where the chains will be installed. Ensure the anchors are securely attached to the ground or wall.
4. Installation: Install the parking chains according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring proper tension and alignment. Consider automatic systems for smoother access control.
5. Integration with Access Control: If using automated parking chains, integrate them with access control systems like key cards, remote controls, or license plate recognition technology.
6. Signage: Install clear signage to inform users about the presence of parking chains and how to operate them.
7. Testing: Test the parking chains’ movement to ensure they raise and lower smoothly without obstructions or jams.
8. Training: Provide training to parking attendants or personnel responsible for operating the chains to ensure proper use and maintenance.
9. Regular Maintenance: Develop a maintenance schedule and conduct regular inspections to keep the parking chains in good working condition.
10. Consider Advanced Features: Depending on the facility’s requirements, consider retrofitting smart parking chains with advanced features like mobile app integration or reservation systems for enhanced security and convenience.
Retrofitting car parking chains allows existing parking facilities to upgrade their security measures efficiently, enhancing access control and providing a safer parking environment for users.

Are there any regulations or guidelines regarding the installation and use of car parking chains in public and private parking lots?
Yes, the installation and use of car parking chains in public and private parking lots are subject to various regulations and guidelines to ensure safety, accessibility, and compliance with local laws. Here are some common considerations:
1. Building Codes and Zoning Regulations: Before installing parking chains, property owners or operators must comply with local building codes and zoning regulations that dictate the types of barriers and access control mechanisms allowed in specific areas.
2. Accessibility Requirements: Parking facilities, including those using parking chains, must comply with accessibility standards, ensuring that they are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This may involve providing designated accessible parking spaces and ensuring barrier-free access to the facility.
3. Height and Clearance: There are often regulations regarding the height of parking chains to prevent them from interfering with vehicles and causing damage. Adequate clearance must be maintained to ensure smooth entry and exit of vehicles.
4. Visibility and Signage: Proper signage should be displayed to inform users about the parking control system in place and to direct them on how to operate it. Adequate lighting should also be provided to ensure good visibility, especially during low-light conditions.
5. Safety Measures: Safety should be a priority when installing parking chains. This includes ensuring that the chain and its supports are securely anchored to prevent accidents or unauthorized removal.
6. Fire Safety Regulations: In certain areas, there may be specific fire safety regulations that dictate the use of specific materials or the inclusion of fire lanes for emergency vehicle access.
7. Permits and Approvals: Depending on the location and local regulations, obtaining permits and approvals from relevant authorities may be necessary before installing parking chains.
8. Compliance with Industry Standards: Manufacturers and installers of parking chains should ensure that their products meet industry standards for quality, durability, and safety.
It is essential for property owners, facility managers, and operators to familiarize themselves with the specific regulations and guidelines in their area and to work with reputable suppliers and installers to ensure compliance and the safe and effective use of car parking chains.

What are the standard sizes and configurations available for car parking chains?
Car parking chains come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different parking facility needs. The standard sizes and configurations include:
1. Length: Parking chains are available in different lengths to span across various entrance or exit widths. Common lengths range from 10 feet (3 meters) to 20 feet (6 meters) to cover typical driveway widths.
2. Link Diameter: The diameter of the individual chain links can vary, with common sizes being around 1/4 inch (6mm) to 3/8 inch (10mm). Thicker links provide additional strength and durability.
3. Material: Parking chains are usually made from sturdy metals like steel, which ensures they can withstand outdoor conditions and the weight of vehicles.
4. Color: While the most common color for parking chains is standard metal silver, some manufacturers offer chains with colored coatings for aesthetic purposes or enhanced visibility.
5. Configurations: There are two primary configurations of parking chains:
- Fixed: Fixed parking chains are permanently mounted on sturdy posts or walls on either side of the entrance or exit. They are not adjustable in length and remain in place at all times.
- Retractable: Retractable or removable parking chains can be raised or lowered as needed. They are connected to retractable posts or bollards, allowing attendants or automated systems to control access by raising or lowering the chain.
It’s essential to choose the appropriate size and configuration based on the specific requirements of the parking facility, the expected volume of traffic, and the level of security needed.


editor by CX 2023-10-18
China OEM Martin Gearbox Short-Pitch 36A-2 Precision Industrial Machinery Roller Chains for Car Parking and Excavator
Product Description
Basic Info
|
ANSI NO: |
180-2R |
DIN/ISO NO: |
36A-2 |
|
Pitch (mm): |
57.1500 |
Roller Diameter(mm): |
35.71 |
|
Inner Plate Width (mm): |
35.48 |
Average Tensile Strength: |
722.2KN |
|
Pin Diameter(mm): |
17.46 |
Plate Thickness (mm): |
7.20 |
|
Weight / Meter (kgs/m): |
13.45 |
Chain Size: |
5F, 10F, 5Meters |
|
Origin: |
HangZhou China |
HS Code: |
7315119000 |
1. Providing 10 series more than 8000 models of chains,Heavy duty engineering chains, oil field chains, heavy duty port crane chains, metallurgy conveyor chains, ultra-high tension escalator chains, mining chains, etc, and customized solutions.
2. More than 80% of our roller chain are exported to all over the world, We are serving customers of top 5 of world famous manufacturers , and more than 90% of our turnover are from the cooperation with the manufacturers in the world.
3. Having advanced online inspection for automatic assembly lines.
4. Having nation level Enterprise Technology Center, we cost no less than 13% of our annual turnover investment in R&D each year.
5. Having our own Standardization Management Committee in our company, and participated in the formulation and modification of the roller chain standards of the People’s Republic of China.
SMCC roller chain is 1 of the most widely used and welcome products in the market. Its continuous innovative development is suitable to be the solutions for many conditions, standard roller chains, motorcycle driving chain, O-ring motorcycle chain, high strength roller chain, conveyor chains, agricultural driving chain, galvanized chain, nickel-plated chain, lubrication-free chain and oilfield chain etc
Our CHINAMFG chain was produced by machinery processing from raw materials to finished products and a full set of quality testing equipment. Mechanical processing equipment include grinding machines, high speed punching machines, milling machines, high speed automatic rolling and assembling machine. Heat treatment was processed by continuous mesh belt conveyor furnace, mesh belt conveyor annealing furnace, advanced central control system of heat treatment, rotary CHINAMFG for chain component heat treatment, which ensure the stability and consistency of the key function of chain components.
We are the best suppliers of Chinese largest palletizing robot enterprises. These items are durable quality with affordable prices, replace of Japan chains, ZheJiang chains exported to Europe, America, Asia and other countries and regions.
Workshop Show
ROLLER CHAIN
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CHAIN
Two different sizes of roller chain, showing construction.
There are 2 types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having 2 inner plates held together by 2 sleeves or bushings CHINAMFG which rotate 2 rollers. Inner links alternate with the second type, the outer links, consisting of 2 outer plates held together by pins passing through the bushings of the inner links. The “bushingless” roller chain is similar in operation though not in construction; instead of separate bushings or sleeves holding the inner plates together, the plate has a tube stamped into it protruding from the hole which serves the same purpose. This has the advantage of removing 1 step in assembly of the chain.
The roller chain design reduces friction compared to simpler designs, resulting in higher efficiency and less wear. The original power transmission chain varieties lacked rollers and bushings, with both the inner and outer plates held by pins which directly contacted the sprocket teeth; however this configuration exhibited extremely rapid wear of both the sprocket teeth, and the plates where they pivoted on the pins. This problem was partially solved by the development of bushed chains, with the pins holding the outer plates passing through bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This distributed the wear over a greater area; however the teeth of the sprockets still wore more rapidly than is desirable, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and provided rolling contact with the teeth of the sprockets resulting in excellent resistance to wear of both sprockets and chain as well. There is even very low friction, as long as the chain is sufficiently lubricated. Continuous, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of primary importance for efficient operation as well as correct tensioning.
LUBRICATION
Many driving chains (for example, in factory equipment, or driving a camshaft inside an internal combustion engine) operate in clean environments, and thus the wearing surfaces (that is, the pins and bushings) are safe from precipitation and airborne grit, many even in a sealed environment such as an oil bath. Some roller chains are designed to have o-rings built into the space between the outside link plate and the inside roller link plates. Chain manufacturers began to include this feature in 1971 after the application was invented by Joseph Montano while working for Whitney Chain of Hartford, Connecticut. O-rings were included as a way to improve lubrication to the links of power transmission chains, a service that is vitally important to extending their working life. These rubber fixtures form a barrier that holds factory applied lubricating grease inside the pin and bushing wear areas. Further, the rubber o-rings prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering inside the chain linkages, where such particles would otherwise cause significant wear.[citation needed]
There are also many chains that have to operate in dirty conditions, and for size or operational reasons cannot be sealed. Examples include chains on farm equipment, bicycles, and chain saws. These chains will necessarily have relatively high rates of wear, particularly when the operators are prepared to accept more friction, less efficiency, more noise and more frequent replacement as they neglect lubrication and adjustment.
Many oil-based lubricants attract dirt and other particles, eventually forming an CHINAMFG paste that will compound wear on chains. This problem can be circumvented by use of a “dry” PTFE spray, which forms a solid film after application and repels both particles and moisture.
VARIANTS DESIGN
Layout of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Inner plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller
If the chain is not being used for a high wear application (for instance if it is just transmitting motion from a hand-operated lever to a control shaft on a machine, or a sliding door on an oven), then 1 of the simpler types of chain may still be used. Conversely, where extra strength but the smooth drive of a smaller pitch is required, the chain may be “siamesed”; instead of just 2 rows of plates on the outer sides of the chain, there may be 3 (“duplex”), 4 (“triplex”), or more rows of plates running parallel, with bushings and rollers between each adjacent pair, and the same number of rows of teeth running in parallel on the sprockets to match. Timing chains on automotive engines, for example, typically have multiple rows of plates called strands.
Roller chain is made in several sizes, the most common American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards being 40, 50, 60, and 80. The first digit(s) indicate the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the last digit being 0 for standard chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. Thus, a chain with half-inch pitch would be a #40 while a #160 sprocket would have teeth spaced 2 inches apart, etc. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch; thus a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but stainless steel is used in food processing machinery or other places where lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are occasionally seen for the same reason.
Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up using a master link (also known as a connecting link), which typically has 1 pin held by a horseshoe clip rather than friction fit, allowing it to be inserted or removed with simple tools. Chain with a removable link or pin is also known as cottered chain, which allows the length of the chain to be adjusted. Half links (also known as offsets) are available and are used to increase the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the master link (also known as a connecting link) “riveted” or mashed on the ends. These pins are made to be durable and are not removable.
USE
An example of 2 ‘ghost’ sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain system
Roller chains are used in low- to mid-speed drives at around 600 to 800 feet per minute; however, at higher speeds, around 2,000 to 3,000 feet per minute, V-belts are normally used due to wear and noise issues.
A bicycle chain is a form of roller chain. Bicycle chains may have a master link, or may require a chain tool for removal and installation. A similar but larger and thus stronger chain is used on most motorcycles although it is sometimes replaced by either a toothed belt or a shaft drive, which offer lower noise level and fewer maintenance requirements.
The great majority of automobile engines use roller chains to drive the camshaft(s). Very high performance engines often use gear drive, and starting in the early 1960s toothed belts were used by some manufacturers.
Chains are also used in forklifts using hydraulic rams as a pulley to raise and lower the carriage; however, these chains are not considered roller chains, but are classified as lift or leaf chains.
Chainsaw cutting chains superficially resemble roller chains but are more closely related to leaf chains. They are driven by projecting drive links which also serve to locate the chain CHINAMFG the bar.
Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 front (cold) vector thrust nozzle – the nozzle is rotated by a chain drive from an air motor
A perhaps unusual use of a pair of motorcycle chains is in the Harrier Jump Jet, where a chain drive from an air motor is used to rotate the movable engine nozzles, allowing them to be pointed downwards for hovering flight, or to the rear for normal CHINAMFG flight, a system known as Thrust vectoring.
WEAR
The effect of wear on a roller chain is to increase the pitch (spacing of the links), causing the chain to grow longer. Note that this is due to wear at the pivoting pins and bushes, not from actual stretching of the metal (as does happen to some flexible steel components such as the hand-brake cable of a motor vehicle).
With modern chains it is unusual for a chain (other than that of a bicycle) to wear until it breaks, since a worn chain leads to the rapid onset of wear on the teeth of the sprockets, with ultimate failure being the loss of all the teeth on the sprocket. The sprockets (in particular the smaller of the two) suffer a grinding motion that puts a characteristic hook shape into the driven face of the teeth. (This effect is made worse by a chain improperly tensioned, but is unavoidable no matter what care is taken). The worn teeth (and chain) no longer provides smooth transmission of power and this may become evident from the noise, the vibration or (in car engines using a timing chain) the variation in ignition timing seen with a timing light. Both sprockets and chain should be replaced in these cases, since a new chain on worn sprockets will not last long. However, in less severe cases it may be possible to save the larger of the 2 sprockets, since it is always the smaller 1 that suffers the most wear. Only in very light-weight applications such as a bicycle, or in extreme cases of improper tension, will the chain normally jump off the sprockets.
The lengthening due to wear of a chain is calculated by the following formula:
M = the length of a number of links measured
S = the number of links measured
P = Pitch
In industry, it is usual to monitor the movement of the chain tensioner (whether manual or automatic) or the exact length of a drive chain (one rule of thumb is to replace a roller chain which has elongated 3% on an adjustable drive or 1.5% on a fixed-center drive). A simpler method, particularly suitable for the cycle or motorcycle user, is to attempt to pull the chain away from the larger of the 2 sprockets, whilst ensuring the chain is taut. Any significant movement (e.g. making it possible to see through a gap) probably indicates a chain worn up to and beyond the limit. Sprocket damage will result if the problem is ignored. Sprocket wear cancels this effect, and may mask chain wear.
CHAIN STRENGTH
The most common measure of roller chain’s strength is tensile strength. Tensile strength represents how much load a chain can withstand under a one-time load before breaking. Just as important as tensile strength is a chain’s fatigue strength. The critical factors in a chain’s fatigue strength is the quality of steel used to manufacture the chain, the heat treatment of the chain components, the quality of the pitch hole fabrication of the linkplates, and the type of shot plus the intensity of shot peen coverage on the linkplates. Other factors can include the thickness of the linkplates and the design (contour) of the linkplates. The rule of thumb for roller chain operating on a continuous drive is for the chain load to not exceed a mere 1/6 or 1/9 of the chain’s tensile strength, depending on the type of master links used (press-fit vs. slip-fit)[citation needed]. Roller chains operating on a continuous drive beyond these thresholds can and typically do fail prematurely via linkplate fatigue failure.
The standard minimum ultimate strength of the ANSI 29.1 steel chain is 12,500 x (pitch, in inches)2. X-ring and O-Ring chains greatly decrease wear by means of internal lubricants, increasing chain life. The internal lubrication is inserted by means of a vacuum when riveting the chain together.
CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An “H” following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, “10 speed chain”. Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2″ x 1/8″ chains, where 1/8″ refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CHINAMFG Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CHINAMFG range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
| Production Scope: | Parts Production Line |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Automation: | Automation |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|


Can car parking chains be integrated with access control systems, such as key cards or remote controls?
Yes, car parking chains can be integrated with access control systems, allowing for more efficient and convenient vehicle access in parking facilities. Integration with access control systems offers several benefits:
1. Key Cards: Parking chains can be linked to electronic access control systems that use key cards or RFID tags. Authorized users are provided with key cards that they can swipe or tap at the entrance to raise the chain, granting them access to the parking area.
2. Remote Controls: In automated parking chains, remote controls can be used to raise or lower the chains. This is particularly useful for parking attendants or personnel who can remotely manage vehicle access from a central location, reducing the need for physical presence at the entrance.
3. Electronic Passes: Some parking facilities issue electronic passes to authorized users. These passes can be read by sensors at the entrance, automatically raising the chain to allow access without the need for manual operation.
4. License Plate Recognition: Advanced access control systems may use license plate recognition technology to automatically identify and grant access to pre-registered vehicles as they approach the entrance, eliminating the need for physical cards or passes.
5. Time-Based Access: Access control systems can be configured to grant access only during specific times or days. This is particularly useful for parking facilities with restricted access hours or reserved parking spaces for certain users.
6. Enhanced Security: Integration with access control systems improves security by ensuring that only authorized vehicles can enter the parking area, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or parking violations.
7. Efficient Traffic Management: Automated access control systems can process vehicles more quickly, reducing waiting times and traffic congestion at the entrance during peak hours.
By integrating car parking chains with access control systems, parking facilities can enhance security, improve user experience, and efficiently manage vehicle access, making it a popular choice for modern parking facilities.

How do I choose the right car parking chain for my parking facility based on traffic volume and vehicle types?
Choosing the right car parking chain for your parking facility involves considering the traffic volume and types of vehicles that will use the facility. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Traffic Volume:
– For high-traffic areas with a significant number of vehicles entering and exiting frequently, consider a durable and heavy-duty parking chain made from materials like steel or stainless steel. These materials can withstand the wear and tear associated with frequent use.
– For low-traffic areas or temporary parking setups, lighter materials like plastic or PVC chains may be suitable as they are more cost-effective.
2. Vehicle Types:
– For standard passenger cars and small vehicles, most parking chains should be sufficient. However, consider the length of the chain to accommodate wider entry points.
– For larger vehicles, such as trucks or buses, ensure that the parking chain is robust enough to support their weight and size. Opt for heavy-duty chains with thicker links and higher load-bearing capacity.
3. Manual vs. Automatic:
– Manual parking chains operated by attendants may be suitable for smaller parking facilities with moderate traffic. They offer a cost-effective and simple access control solution.
– Automatic parking chains integrated with electronic access control systems are more suitable for larger parking facilities or those with high traffic volume. They provide faster and more efficient access control, minimizing waiting times.
4. Customization:
– Consider whether you require customized parking chains to fit specific dimensions or to align with the overall aesthetic of the parking facility.
5. Environmental Factors:
– For outdoor parking facilities exposed to harsh weather conditions, opt for materials that offer good corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel or aluminum.
6. Budget:
– Determine the budget available for the parking chains, considering both the initial investment and long-term maintenance costs.
7. Compliance:
– Ensure that the chosen parking chains comply with local regulations and accessibility requirements to provide a safe and accessible parking environment.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select the most appropriate car parking chain that aligns with your parking facility’s specific needs, ensuring efficient access control and a positive user experience for all vehicle types and traffic volumes.

How do car parking chains enhance security and prevent unauthorized access to parking areas?
Car parking chains serve as a physical barrier and play a crucial role in enhancing security and preventing unauthorized access to parking areas. Here’s how they achieve this:
1. Physical Deterrent: The presence of a chain across the entrance acts as a visual deterrent, dissuading unauthorized vehicles from attempting to enter the parking area. It signals that the area is controlled and restricted to authorized personnel only.
2. Controlled Access: Parking chains are manually operated or integrated with electronic access control systems. Only authorized users with the appropriate credentials, such as a key, keycard, or remote control, can raise or lower the chain to gain access.
3. Preventing Tailgating: In manual systems, parking attendants can visually verify each vehicle’s authorization before allowing entry. In automatic systems, the access control technology ensures that only one vehicle is allowed to pass at a time, preventing unauthorized vehicles from tailgating behind an authorized one.
4. Flexible Access Control: Some parking chains can be integrated with electronic access control systems that allow for fine-grained control. This includes time-based access permissions or specific access rights for different user groups, enhancing security measures.
5. Cost-Effective Security: Compared to more advanced access control systems like automated gates or barrier arms, parking chains offer a cost-effective security solution, making them suitable for various parking facilities.
6. Reducing Vehicle Theft: By restricting access to only authorized vehicles, parking chains reduce the risk of theft or unauthorized use of parked vehicles.
7. Minimizing Traffic Violations: Parking chains prevent unauthorized parking, reducing instances of illegal parking or traffic violations within the parking area.
8. Additional Security Measures: Parking chains can be complemented with other security features like surveillance cameras, lighting, and manned security personnel, creating a comprehensive security strategy for the parking facility.
In summary, car parking chains provide a simple yet effective method to control access, enhance security, and prevent unauthorized entry into parking areas, ensuring a safer and more controlled environment for vehicles and users.


editor by CX 2023-10-17
China best Martin Gearbox Short-Pitch 36A-2 Precision Industrial Machinery Roller Chains for Car Parking and Excavator
Product Description
Basic Info
|
ANSI NO: |
180-2R |
DIN/ISO NO: |
36A-2 |
|
Pitch (mm): |
57.1500 |
Roller Diameter(mm): |
35.71 |
|
Inner Plate Width (mm): |
35.48 |
Average Tensile Strength: |
722.2KN |
|
Pin Diameter(mm): |
17.46 |
Plate Thickness (mm): |
7.20 |
|
Weight / Meter (kgs/m): |
13.45 |
Chain Size: |
5F, 10F, 5Meters |
|
Origin: |
HangZhou China |
HS Code: |
7315119000 |
1. Providing 10 series more than 8000 models of chains,Heavy duty engineering chains, oil field chains, heavy duty port crane chains, metallurgy conveyor chains, ultra-high tension escalator chains, mining chains, etc, and customized solutions.
2. More than 80% of our roller chain are exported to all over the world, We are serving customers of top 5 of world famous manufacturers , and more than 90% of our turnover are from the cooperation with the manufacturers in the world.
3. Having advanced online inspection for automatic assembly lines.
4. Having nation level Enterprise Technology Center, we cost no less than 13% of our annual turnover investment in R&D each year.
5. Having our own Standardization Management Committee in our company, and participated in the formulation and modification of the roller chain standards of the People’s Republic of China.
SMCC roller chain is 1 of the most widely used and welcome products in the market. Its continuous innovative development is suitable to be the solutions for many conditions, standard roller chains, motorcycle driving chain, O-ring motorcycle chain, high strength roller chain, conveyor chains, agricultural driving chain, galvanized chain, nickel-plated chain, lubrication-free chain and oilfield chain etc
Our CZPT chain was produced by machinery processing from raw materials to finished products and a full set of quality testing equipment. Mechanical processing equipment include grinding machines, high speed punching machines, milling machines, high speed automatic rolling and assembling machine. Heat treatment was processed by continuous mesh belt conveyor furnace, mesh belt conveyor annealing furnace, advanced central control system of heat treatment, rotary CZPT for chain component heat treatment, which ensure the stability and consistency of the key function of chain components.
We are the best suppliers of Chinese largest palletizing robot enterprises. These items are durable quality with affordable prices, replace of Japan chains, ZheJiang chains exported to Europe, America, Asia and other countries and regions.
Workshop Show
ROLLER CHAIN
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CHAIN
Two different sizes of roller chain, showing construction.
There are 2 types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having 2 inner plates held together by 2 sleeves or bushings CZPT which rotate 2 rollers. Inner links alternate with the second type, the outer links, consisting of 2 outer plates held together by pins passing through the bushings of the inner links. The “bushingless” roller chain is similar in operation though not in construction; instead of separate bushings or sleeves holding the inner plates together, the plate has a tube stamped into it protruding from the hole which serves the same purpose. This has the advantage of removing 1 step in assembly of the chain.
The roller chain design reduces friction compared to simpler designs, resulting in higher efficiency and less wear. The original power transmission chain varieties lacked rollers and bushings, with both the inner and outer plates held by pins which directly contacted the sprocket teeth; however this configuration exhibited extremely rapid wear of both the sprocket teeth, and the plates where they pivoted on the pins. This problem was partially solved by the development of bushed chains, with the pins holding the outer plates passing through bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This distributed the wear over a greater area; however the teeth of the sprockets still wore more rapidly than is desirable, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and provided rolling contact with the teeth of the sprockets resulting in excellent resistance to wear of both sprockets and chain as well. There is even very low friction, as long as the chain is sufficiently lubricated. Continuous, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of primary importance for efficient operation as well as correct tensioning.
LUBRICATION
Many driving chains (for example, in factory equipment, or driving a camshaft inside an internal combustion engine) operate in clean environments, and thus the wearing surfaces (that is, the pins and bushings) are safe from precipitation and airborne grit, many even in a sealed environment such as an oil bath. Some roller chains are designed to have o-rings built into the space between the outside link plate and the inside roller link plates. Chain manufacturers began to include this feature in 1971 after the application was invented by Joseph Montano while working for Whitney Chain of Hartford, Connecticut. O-rings were included as a way to improve lubrication to the links of power transmission chains, a service that is vitally important to extending their working life. These rubber fixtures form a barrier that holds factory applied lubricating grease inside the pin and bushing wear areas. Further, the rubber o-rings prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering inside the chain linkages, where such particles would otherwise cause significant wear.[citation needed]
There are also many chains that have to operate in dirty conditions, and for size or operational reasons cannot be sealed. Examples include chains on farm equipment, bicycles, and chain saws. These chains will necessarily have relatively high rates of wear, particularly when the operators are prepared to accept more friction, less efficiency, more noise and more frequent replacement as they neglect lubrication and adjustment.
Many oil-based lubricants attract dirt and other particles, eventually forming an CZPT paste that will compound wear on chains. This problem can be circumvented by use of a “dry” PTFE spray, which forms a solid film after application and repels both particles and moisture.
VARIANTS DESIGN
Layout of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Inner plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller
If the chain is not being used for a high wear application (for instance if it is just transmitting motion from a hand-operated lever to a control shaft on a machine, or a sliding door on an oven), then 1 of the simpler types of chain may still be used. Conversely, where extra strength but the smooth drive of a smaller pitch is required, the chain may be “siamesed”; instead of just 2 rows of plates on the outer sides of the chain, there may be 3 (“duplex”), 4 (“triplex”), or more rows of plates running parallel, with bushings and rollers between each adjacent pair, and the same number of rows of teeth running in parallel on the sprockets to match. Timing chains on automotive engines, for example, typically have multiple rows of plates called strands.
Roller chain is made in several sizes, the most common American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards being 40, 50, 60, and 80. The first digit(s) indicate the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the last digit being 0 for standard chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. Thus, a chain with half-inch pitch would be a #40 while a #160 sprocket would have teeth spaced 2 inches apart, etc. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch; thus a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but stainless steel is used in food processing machinery or other places where lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are occasionally seen for the same reason.
Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up using a master link (also known as a connecting link), which typically has 1 pin held by a horseshoe clip rather than friction fit, allowing it to be inserted or removed with simple tools. Chain with a removable link or pin is also known as cottered chain, which allows the length of the chain to be adjusted. Half links (also known as offsets) are available and are used to increase the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the master link (also known as a connecting link) “riveted” or mashed on the ends. These pins are made to be durable and are not removable.
USE
An example of 2 ‘ghost’ sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain system
Roller chains are used in low- to mid-speed drives at around 600 to 800 feet per minute; however, at higher speeds, around 2,000 to 3,000 feet per minute, V-belts are normally used due to wear and noise issues.
A bicycle chain is a form of roller chain. Bicycle chains may have a master link, or may require a chain tool for removal and installation. A similar but larger and thus stronger chain is used on most motorcycles although it is sometimes replaced by either a toothed belt or a shaft drive, which offer lower noise level and fewer maintenance requirements.
The great majority of automobile engines use roller chains to drive the camshaft(s). Very high performance engines often use gear drive, and starting in the early 1960s toothed belts were used by some manufacturers.
Chains are also used in forklifts using hydraulic rams as a pulley to raise and lower the carriage; however, these chains are not considered roller chains, but are classified as lift or leaf chains.
Chainsaw cutting chains superficially resemble roller chains but are more closely related to leaf chains. They are driven by projecting drive links which also serve to locate the chain CZPT the bar.
Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 front (cold) vector thrust nozzle – the nozzle is rotated by a chain drive from an air motor
A perhaps unusual use of a pair of motorcycle chains is in the Harrier Jump Jet, where a chain drive from an air motor is used to rotate the movable engine nozzles, allowing them to be pointed downwards for hovering flight, or to the rear for normal CZPT flight, a system known as Thrust vectoring.
WEAR
The effect of wear on a roller chain is to increase the pitch (spacing of the links), causing the chain to grow longer. Note that this is due to wear at the pivoting pins and bushes, not from actual stretching of the metal (as does happen to some flexible steel components such as the hand-brake cable of a motor vehicle).
With modern chains it is unusual for a chain (other than that of a bicycle) to wear until it breaks, since a worn chain leads to the rapid onset of wear on the teeth of the sprockets, with ultimate failure being the loss of all the teeth on the sprocket. The sprockets (in particular the smaller of the two) suffer a grinding motion that puts a characteristic hook shape into the driven face of the teeth. (This effect is made worse by a chain improperly tensioned, but is unavoidable no matter what care is taken). The worn teeth (and chain) no longer provides smooth transmission of power and this may become evident from the noise, the vibration or (in car engines using a timing chain) the variation in ignition timing seen with a timing light. Both sprockets and chain should be replaced in these cases, since a new chain on worn sprockets will not last long. However, in less severe cases it may be possible to save the larger of the 2 sprockets, since it is always the smaller 1 that suffers the most wear. Only in very light-weight applications such as a bicycle, or in extreme cases of improper tension, will the chain normally jump off the sprockets.
The lengthening due to wear of a chain is calculated by the following formula:
M = the length of a number of links measured
S = the number of links measured
P = Pitch
In industry, it is usual to monitor the movement of the chain tensioner (whether manual or automatic) or the exact length of a drive chain (one rule of thumb is to replace a roller chain which has elongated 3% on an adjustable drive or 1.5% on a fixed-center drive). A simpler method, particularly suitable for the cycle or motorcycle user, is to attempt to pull the chain away from the larger of the 2 sprockets, whilst ensuring the chain is taut. Any significant movement (e.g. making it possible to see through a gap) probably indicates a chain worn up to and beyond the limit. Sprocket damage will result if the problem is ignored. Sprocket wear cancels this effect, and may mask chain wear.
CHAIN STRENGTH
The most common measure of roller chain’s strength is tensile strength. Tensile strength represents how much load a chain can withstand under a one-time load before breaking. Just as important as tensile strength is a chain’s fatigue strength. The critical factors in a chain’s fatigue strength is the quality of steel used to manufacture the chain, the heat treatment of the chain components, the quality of the pitch hole fabrication of the linkplates, and the type of shot plus the intensity of shot peen coverage on the linkplates. Other factors can include the thickness of the linkplates and the design (contour) of the linkplates. The rule of thumb for roller chain operating on a continuous drive is for the chain load to not exceed a mere 1/6 or 1/9 of the chain’s tensile strength, depending on the type of master links used (press-fit vs. slip-fit)[citation needed]. Roller chains operating on a continuous drive beyond these thresholds can and typically do fail prematurely via linkplate fatigue failure.
The standard minimum ultimate strength of the ANSI 29.1 steel chain is 12,500 x (pitch, in inches)2. X-ring and O-Ring chains greatly decrease wear by means of internal lubricants, increasing chain life. The internal lubrication is inserted by means of a vacuum when riveting the chain together.
CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An “H” following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, “10 speed chain”. Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2″ x 1/8″ chains, where 1/8″ refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CZPT Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CZPT range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Transmission Type: | Flexible |
| Automatic Production Line: | Comprehensive |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|


Can car parking chains be integrated with access control systems, such as key cards or remote controls?
Yes, car parking chains can be integrated with access control systems, allowing for more efficient and convenient vehicle access in parking facilities. Integration with access control systems offers several benefits:
1. Key Cards: Parking chains can be linked to electronic access control systems that use key cards or RFID tags. Authorized users are provided with key cards that they can swipe or tap at the entrance to raise the chain, granting them access to the parking area.
2. Remote Controls: In automated parking chains, remote controls can be used to raise or lower the chains. This is particularly useful for parking attendants or personnel who can remotely manage vehicle access from a central location, reducing the need for physical presence at the entrance.
3. Electronic Passes: Some parking facilities issue electronic passes to authorized users. These passes can be read by sensors at the entrance, automatically raising the chain to allow access without the need for manual operation.
4. License Plate Recognition: Advanced access control systems may use license plate recognition technology to automatically identify and grant access to pre-registered vehicles as they approach the entrance, eliminating the need for physical cards or passes.
5. Time-Based Access: Access control systems can be configured to grant access only during specific times or days. This is particularly useful for parking facilities with restricted access hours or reserved parking spaces for certain users.
6. Enhanced Security: Integration with access control systems improves security by ensuring that only authorized vehicles can enter the parking area, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or parking violations.
7. Efficient Traffic Management: Automated access control systems can process vehicles more quickly, reducing waiting times and traffic congestion at the entrance during peak hours.
By integrating car parking chains with access control systems, parking facilities can enhance security, improve user experience, and efficiently manage vehicle access, making it a popular choice for modern parking facilities.

What materials are commonly used to manufacture car parking chains, and how do they affect durability and performance?
Car parking chains are typically manufactured using various materials, and the choice of material can significantly impact the durability and performance of the chains. The most common materials used include:
1. Steel: Steel is the most prevalent material for parking chains due to its high strength and durability. It can withstand heavy loads and resist wear and tear, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. Steel chains are often coated or galvanized to enhance their corrosion resistance and extend their lifespan.
2. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel chains offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for parking areas in coastal or high-humidity environments. They are less prone to rust and maintain their appearance over time.
3. Plastic or PVC: Plastic or PVC chains are lightweight and cost-effective alternatives to metal chains. While they may not be as strong as steel, they are suitable for low-traffic areas and temporary parking setups. However, they may be less durable and require more frequent replacement compared to metal chains.
4. Brass: Brass chains are sometimes used for their aesthetic appeal, as they have a distinct gold-like appearance. However, they are not as commonly used as steel or stainless steel due to their higher cost and lower strength.
5. Aluminum: Aluminum chains are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for outdoor use. However, they are not as strong as steel or stainless steel, and their use is often limited to less demanding applications.
The choice of material depends on several factors, including the intended usage, environmental conditions, budget constraints, and aesthetic preferences. Steel and stainless steel are the most popular choices for parking chains as they offer a good balance of strength, durability, and resistance to various weather conditions. Plastic or PVC chains are more suitable for temporary setups or situations where cost is a primary concern.
Regular maintenance and proper care, regardless of the material used, will also contribute to the longevity and performance of car parking chains. Periodic inspections, lubrication, and prompt repair of any damage are essential to ensure the chains function effectively and provide reliable access control in parking facilities.

What is a car parking chain, and how is it used in parking facilities and garages?
A car parking chain is a mechanical barrier used in parking facilities and garages to control vehicle access and prevent unauthorized entry. It consists of a sturdy metal chain suspended across the entrance or exit of a parking area.
The chain is connected to two sturdy posts or walls on either side of the entrance. When lowered, the chain obstructs the passage of vehicles, restricting their entry or exit. Conversely, when lifted, it allows authorized vehicles to pass through.
Parking chains are commonly used in places where a more sophisticated access control system like a gate or a barrier arm may not be necessary. They offer a simple and cost-effective solution for managing vehicle flow.
Typically, parking facility attendants or authorized personnel are responsible for controlling the car parking chain. They manually raise and lower the chain using a key or a specialized lock system.
In some cases, modern parking chains may be automated and integrated with access control systems. This can include keycard readers, electronic passes, or even remote-controlled mechanisms, making it more convenient for authorized users to enter and exit the parking area.
Overall, car parking chains serve as a physical deterrent to prevent unauthorized access and ensure better control over vehicle movement in parking facilities and garages.
“`

editor by CX 2023-09-11
China Hot selling Short-Pitch 16A Precision Industrial & Agricultural General Hardware Martin Sugar/Coal Machine/Car Parking Transmission Driving Roller Chains
Product Description
Basic Info
|
ANSI NO: |
80 |
DIN/ISO NO: |
16A |
|
Pitch (mm): |
25.40 |
Roller Diameter(mm): |
15.88 |
|
Pin Diameter(mm): |
7.92 |
Plate Thickness (mm): |
3.25 |
|
Inner Plate Width (mm): |
15.75 |
Average Tensile Strength: |
69.4KN |
|
Chain Size: |
5F, 10F, 5Meters |
Weight / Meter (kgs/m): |
2.60 |
|
Origin: |
HangZhou China |
HS Code: |
7315119000 |
ROLLER CHAIN
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CHAIN
Two different sizes of roller chain, showing construction.
There are 2 types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having 2 inner plates held together by 2 sleeves or bushings CZPT which rotate 2 rollers. Inner links alternate with the second type, the outer links, consisting of 2 outer plates held together by pins passing through the bushings of the inner links. The “bushingless” roller chain is similar in operation though not in construction; instead of separate bushings or sleeves holding the inner plates together, the plate has a tube stamped into it protruding from the hole which serves the same purpose. This has the advantage of removing 1 step in assembly of the chain.
The roller chain design reduces friction compared to simpler designs, resulting in higher efficiency and less wear. The original power transmission chain varieties lacked rollers and bushings, with both the inner and outer plates held by pins which directly contacted the sprocket teeth; however this configuration exhibited extremely rapid wear of both the sprocket teeth, and the plates where they pivoted on the pins. This problem was partially solved by the development of bushed chains, with the pins holding the outer plates passing through bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This distributed the wear over a greater area; however the teeth of the sprockets still wore more rapidly than is desirable, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and provided rolling contact with the teeth of the sprockets resulting in excellent resistance to wear of both sprockets and chain as well. There is even very low friction, as long as the chain is sufficiently lubricated. Continuous, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of primary importance for efficient operation as well as correct tensioning.
LUBRICATION
Many driving chains (for example, in factory equipment, or driving a camshaft inside an internal combustion engine) operate in clean environments, and thus the wearing surfaces (that is, the pins and bushings) are safe from precipitation and airborne grit, many even in a sealed environment such as an oil bath. Some roller chains are designed to have o-rings built into the space between the outside link plate and the inside roller link plates. Chain manufacturers began to include this feature in 1971 after the application was invented by Joseph Montano while working for Whitney Chain of Hartford, Connecticut. O-rings were included as a way to improve lubrication to the links of power transmission chains, a service that is vitally important to extending their working life. These rubber fixtures form a barrier that holds factory applied lubricating grease inside the pin and bushing wear areas. Further, the rubber o-rings prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering inside the chain linkages, where such particles would otherwise cause significant wear.[citation needed]
There are also many chains that have to operate in dirty conditions, and for size or operational reasons cannot be sealed. Examples include chains on farm equipment, bicycles, and chain saws. These chains will necessarily have relatively high rates of wear, particularly when the operators are prepared to accept more friction, less efficiency, more noise and more frequent replacement as they neglect lubrication and adjustment.
Many oil-based lubricants attract dirt and other particles, eventually forming an CZPT paste that will compound wear on chains. This problem can be circumvented by use of a “dry” PTFE spray, which forms a solid film after application and repels both particles and moisture.
VARIANTS DESIGN
Layout of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Inner plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller
If the chain is not being used for a high wear application (for instance if it is just transmitting motion from a hand-operated lever to a control shaft on a machine, or a sliding door on an oven), then 1 of the simpler types of chain may still be used. Conversely, where extra strength but the smooth drive of a smaller pitch is required, the chain may be “siamesed”; instead of just 2 rows of plates on the outer sides of the chain, there may be 3 (“duplex”), 4 (“triplex”), or more rows of plates running parallel, with bushings and rollers between each adjacent pair, and the same number of rows of teeth running in parallel on the sprockets to match. Timing chains on automotive engines, for example, typically have multiple rows of plates called strands.
Roller chain is made in several sizes, the most common American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards being 40, 50, 60, and 80. The first digit(s) indicate the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the last digit being 0 for standard chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. Thus, a chain with half-inch pitch would be a #40 while a #160 sprocket would have teeth spaced 2 inches apart, etc. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch; thus a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but stainless steel is used in food processing machinery or other places where lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are occasionally seen for the same reason.
Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up using a master link (also known as a connecting link), which typically has 1 pin held by a horseshoe clip rather than friction fit, allowing it to be inserted or removed with simple tools. Chain with a removable link or pin is also known as cottered chain, which allows the length of the chain to be adjusted. Half links (also known as offsets) are available and are used to increase the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the master link (also known as a connecting link) “riveted” or mashed on the ends. These pins are made to be durable and are not removable.
USE
An example of 2 ‘ghost’ sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain system
Roller chains are used in low- to mid-speed drives at around 600 to 800 feet per minute; however, at higher speeds, around 2,000 to 3,000 feet per minute, V-belts are normally used due to wear and noise issues.
A bicycle chain is a form of roller chain. Bicycle chains may have a master link, or may require a chain tool for removal and installation. A similar but larger and thus stronger chain is used on most motorcycles although it is sometimes replaced by either a toothed belt or a shaft drive, which offer lower noise level and fewer maintenance requirements.
The great majority of automobile engines use roller chains to drive the camshaft(s). Very high performance engines often use gear drive, and starting in the early 1960s toothed belts were used by some manufacturers.
Chains are also used in forklifts using hydraulic rams as a pulley to raise and lower the carriage; however, these chains are not considered roller chains, but are classified as lift or leaf chains.
Chainsaw cutting chains superficially resemble roller chains but are more closely related to leaf chains. They are driven by projecting drive links which also serve to locate the chain CZPT the bar.
Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 front (cold) vector thrust nozzle – the nozzle is rotated by a chain drive from an air motor
A perhaps unusual use of a pair of motorcycle chains is in the Harrier Jump Jet, where a chain drive from an air motor is used to rotate the movable engine nozzles, allowing them to be pointed downwards for hovering flight, or to the rear for normal CZPT flight, a system known as Thrust vectoring.
WEAR
The effect of wear on a roller chain is to increase the pitch (spacing of the links), causing the chain to grow longer. Note that this is due to wear at the pivoting pins and bushes, not from actual stretching of the metal (as does happen to some flexible steel components such as the hand-brake cable of a motor vehicle).
With modern chains it is unusual for a chain (other than that of a bicycle) to wear until it breaks, since a worn chain leads to the rapid onset of wear on the teeth of the sprockets, with ultimate failure being the loss of all the teeth on the sprocket. The sprockets (in particular the smaller of the two) suffer a grinding motion that puts a characteristic hook shape into the driven face of the teeth. (This effect is made worse by a chain improperly tensioned, but is unavoidable no matter what care is taken). The worn teeth (and chain) no longer provides smooth transmission of power and this may become evident from the noise, the vibration or (in car engines using a timing chain) the variation in ignition timing seen with a timing light. Both sprockets and chain should be replaced in these cases, since a new chain on worn sprockets will not last long. However, in less severe cases it may be possible to save the larger of the 2 sprockets, since it is always the smaller 1 that suffers the most wear. Only in very light-weight applications such as a bicycle, or in extreme cases of improper tension, will the chain normally jump off the sprockets.
The lengthening due to wear of a chain is calculated by the following formula:
M = the length of a number of links measured
S = the number of links measured
P = Pitch
In industry, it is usual to monitor the movement of the chain tensioner (whether manual or automatic) or the exact length of a drive chain (one rule of thumb is to replace a roller chain which has elongated 3% on an adjustable drive or 1.5% on a fixed-center drive). A simpler method, particularly suitable for the cycle or motorcycle user, is to attempt to pull the chain away from the larger of the 2 sprockets, whilst ensuring the chain is taut. Any significant movement (e.g. making it possible to see through a gap) probably indicates a chain worn up to and beyond the limit. Sprocket damage will result if the problem is ignored. Sprocket wear cancels this effect, and may mask chain wear.
CHAIN STRENGTH
The most common measure of roller chain’s strength is tensile strength. Tensile strength represents how much load a chain can withstand under a one-time load before breaking. Just as important as tensile strength is a chain’s fatigue strength. The critical factors in a chain’s fatigue strength is the quality of steel used to manufacture the chain, the heat treatment of the chain components, the quality of the pitch hole fabrication of the linkplates, and the type of shot plus the intensity of shot peen coverage on the linkplates. Other factors can include the thickness of the linkplates and the design (contour) of the linkplates. The rule of thumb for roller chain operating on a continuous drive is for the chain load to not exceed a mere 1/6 or 1/9 of the chain’s tensile strength, depending on the type of master links used (press-fit vs. slip-fit)[citation needed]. Roller chains operating on a continuous drive beyond these thresholds can and typically do fail prematurely via linkplate fatigue failure.
The standard minimum ultimate strength of the ANSI 29.1 steel chain is 12,500 x (pitch, in inches)2. X-ring and O-Ring chains greatly decrease wear by means of internal lubricants, increasing chain life. The internal lubrication is inserted by means of a vacuum when riveting the chain together.
CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An “H” following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, “10 speed chain”. Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2″ x 1/8″ chains, where 1/8″ refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CZPT Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CZPT range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Transmission Type: | Flexible |
| Automatic Production Line: | Comprehensive |
| Certification: | ISO, CE, LR, ABS |
| Automation: | Automation |
| Flexible Production: | Intelligent Manufacturing |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|


Are there any cost-effective options for car parking chains without compromising on quality and reliability?
Yes, there are cost-effective options for car parking chains that still offer good quality and reliability. While premium materials like stainless steel may be more expensive, several alternatives provide a balance between affordability and performance. Here are some cost-effective options:
1. Galvanized Steel: Galvanized steel chains are coated with a layer of zinc to enhance their corrosion resistance. They are more affordable than stainless steel chains while still offering decent durability and weather resistance.
2. Plastic or PVC Chains: Plastic or PVC chains are often more budget-friendly than metal chains. While they may not be as durable as steel, they can be suitable for low-traffic areas or temporary parking setups.
3. Chain Accessories: Some manufacturers offer cost-effective chain accessories, such as chain hooks, connectors, and tensioners, without compromising on quality. These accessories are essential for proper chain installation and maintenance.
4. Recycled Materials: Some parking chains are made from recycled materials, which can be a cost-effective and eco-friendly option. Recycled steel or other materials can still offer satisfactory performance while reducing the demand for new resources.
5. Long-Lasting Materials: Investing in parking chains made from durable materials, even if slightly more expensive upfront, can be cost-effective in the long run. Chains that last longer and require less frequent replacement can result in cost savings over time.
6. Warranty and Support: Look for suppliers that offer warranties and reliable customer support. A good warranty can provide peace of mind and ensure you get the most value from your investment.
7. Buy in Bulk: If you need multiple parking chains, purchasing in bulk can often lead to discounts or cost savings.
When seeking cost-effective options for car parking chains, consider your specific needs and the expected usage of the chains. It’s essential to strike a balance between affordability and performance, ensuring that the chosen chains meet safety and reliability requirements for your parking facility.

Are there any regulations or guidelines regarding the installation and use of car parking chains in public and private parking lots?
Yes, the installation and use of car parking chains in public and private parking lots are subject to various regulations and guidelines to ensure safety, accessibility, and compliance with local laws. Here are some common considerations:
1. Building Codes and Zoning Regulations: Before installing parking chains, property owners or operators must comply with local building codes and zoning regulations that dictate the types of barriers and access control mechanisms allowed in specific areas.
2. Accessibility Requirements: Parking facilities, including those using parking chains, must comply with accessibility standards, ensuring that they are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This may involve providing designated accessible parking spaces and ensuring barrier-free access to the facility.
3. Height and Clearance: There are often regulations regarding the height of parking chains to prevent them from interfering with vehicles and causing damage. Adequate clearance must be maintained to ensure smooth entry and exit of vehicles.
4. Visibility and Signage: Proper signage should be displayed to inform users about the parking control system in place and to direct them on how to operate it. Adequate lighting should also be provided to ensure good visibility, especially during low-light conditions.
5. Safety Measures: Safety should be a priority when installing parking chains. This includes ensuring that the chain and its supports are securely anchored to prevent accidents or unauthorized removal.
6. Fire Safety Regulations: In certain areas, there may be specific fire safety regulations that dictate the use of specific materials or the inclusion of fire lanes for emergency vehicle access.
7. Permits and Approvals: Depending on the location and local regulations, obtaining permits and approvals from relevant authorities may be necessary before installing parking chains.
8. Compliance with Industry Standards: Manufacturers and installers of parking chains should ensure that their products meet industry standards for quality, durability, and safety.
It is essential for property owners, facility managers, and operators to familiarize themselves with the specific regulations and guidelines in their area and to work with reputable suppliers and installers to ensure compliance and the safe and effective use of car parking chains.

Can car parking chains be customized to fit specific parking space dimensions?
Yes, car parking chains can be customized to fit specific parking space dimensions. Manufacturers often offer customization options to cater to the unique requirements of different parking facilities. Here’s how parking chains can be customized:
1. Length Adjustment: Parking chains can be made to the exact length needed to span across the width of the entrance or exit of a specific parking space. This ensures a proper fit without any excess chain length that could lead to tangling or inconvenience.
2. Chain Link Size: The diameter and thickness of the individual chain links can be adjusted to match the desired strength and aesthetic preferences. Thicker links may be chosen for heavy-duty applications, while thinner links can be used for lighter traffic areas.
3. Color Options: Customization may extend to the color of the parking chain, with some manufacturers offering various color coatings or finishes to suit the parking facility’s design or branding requirements.
4. Retractable Mechanism: For parking areas that require flexible access control, parking chains can be integrated with retractable mechanisms, allowing them to be raised or lowered as needed.
5. Personalized Branding: In some cases, parking chains can be customized with logos or branding elements, particularly for commercial or corporate parking facilities.
6. Material and Coating: While most parking chains are made from steel for durability, specialized materials or coatings can be considered for unique environments, such as coastal areas with high corrosion potential.
Keep in mind that while customization offers tailored solutions, it may also affect the cost and lead time for manufacturing the parking chains. It’s essential to work with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who can provide guidance on the best customization options based on the specific needs of the parking facility.


editor by CX 2023-09-08
China 14K gold plated chains for Jewelry making Necklace accessories brass key link Color retention Paper clip link chain connecting link roller chain
Design Amount: ZJ0128
Jewelry Results Sort: Chains
Identify: Paper clip url chain
Style: Simple
Materials: Brass
Characteristic: Environmental Pleasant
MOQ: 50Yards
Jewelry Sort: Bracelet Areas
Plating: Genuine 18k Gold Plating
Use: Necklace Jewelry Making
Usage: Diy Jewellery Accessory
Shipping and delivery time: 7-15 Days
Merchandise Description
| Product name | chain | ||||||
| Material | Brass | ||||||
| Size | Regular size | ||||||
| Packaging | 50yards/CTN,18*12*10cm/CTN | ||||||
| MOQ | 50yards | ||||||
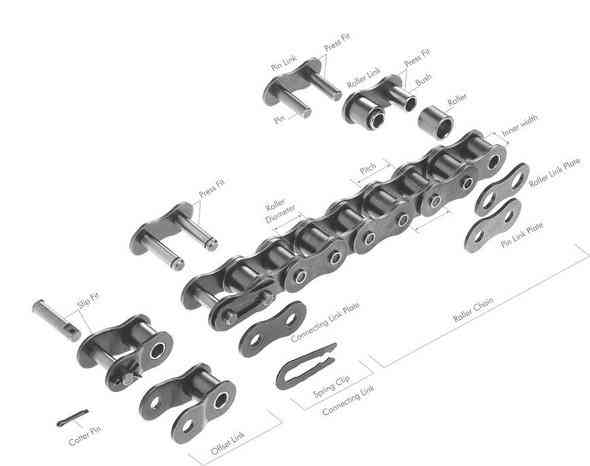
Choosing a drive chain for a belt conveyor
The drive chain is used to move heavy objects on the conveyor chain. Chains are magnetic, antistatic, high temperature, or chemical resistant, depending on the application. These types of drive chains are used in many different industries. A common machine that uses this type of drive is a chain hoist. Chain hoists are designed to lift heavy loads with minimal effort. Chains are often used to transport heavy loads.
roller chain
Whether using a roller chain as a drive chain or a belt conveyor can be tricky. Whether it’s a small low-speed drive with manual lubrication or a high-speed pump-lubricated drive with multiple sprockets, there are several factors to consider when choosing a roller chain. First, you need to consider motor horsepower and rpm. The speed of the motor determines how much chain you need. For example, if you are using a low-speed drive, you will need to choose a low-pitch, high-pitch chain. Another thing to consider is chain length – ideally, you can go for an even number of sprockets and chains, but never go smaller.
The lubrication system is also important because the lubrication system must be able to deliver enough oil. The type of oil used to lubricate a chain depends on its operating environment, temperature and speed. Wear is caused by pressure on the bearing, angular sliding of the pins, and rotation of the rollers. There are five different types of lubrication methods available, depending on the system used. A high-quality carbon steel chain is a major advantage when operating at high temperatures, as it can withstand higher temperatures.
The materials of construction for roller chains vary by application. Typically, the most common materials are steel and stainless steel, but sometimes alloy steels are used in food processing machinery that may have lubrication problems. Nylon and brass are also sometimes used. Some industries require heavy-duty chains. If you need an extremely heavy chain, you may want to consider a heavy-duty roller chain. If you are not sure which type of chain is best for your application, consult an industry expert.
Unlike other chains, roller chains are more efficient from a size and weight perspective. While solution chains are useful in some situations, drive chains are more effective for dirty work and slipping on tracks. They are commonly used in construction and manufacturing. There are other advantages to using a drive chain. They are generally stronger than belts, which is a huge benefit. So, if you’re wondering which is better, here are them:
Multi-strand roller chain
The multi-strand roller chains for drive chains market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 20% during the forecast period. Market reports cover product demand, supply, and cost. The report covers the global market including company profiles, product details, and contact information of key players. It also takes into account the revenue generated by different application areas. The report contains 159 pages of useful information and data. It is an essential tool for anyone involved in drive chain manufacturing.
The essential characteristics of multi-strand chains are their power ratings and allowable bearing area pressures. Power rating is an important characteristic that determines the chain’s ability to transmit a specific load. Typically, multi-strand chains are rated in the range of 12,000 watts per strand. However, their capabilities are limited by link plate fatigue, roller impact fatigue, and wear between pins and bushings.
Energy Series chains are ideal for high-speed and high shock load applications. The chain is designed to provide reliable power and withstand the rigors of the oil and gas industry. It uses high-strength steel and double-coated rolls. These chains come in different lengths and come in two types: single-strand and multi-strand. It is best to consult a professional to find out which chain best suits your needs.
The global multi-strand roller chains market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 7% during the forecast period. From 2011 to 2019, the industry is expected to grow by nearly 6%. However, the outlook for this market is not optimistic, with some companies experiencing negative growth over the past year. Nonetheless, slowing global economic growth and tightening COVID-19 regulations are likely to hinder the market growth.
Although requirements vary by application, it must be remembered that the load on a multi-strand roller chain must not be greater than 1/9 or 1/6 of the tensile strength of the chain. If the load exceeds this threshold, the chainplates will fatigue. This is the main reason why roller chains are expensive. However, this is not always the case. Multi-strand roller chains are a great idea if you are looking for an affordable and reliable drive chain.
double chain
If you’re looking for an industrial-grade drive chain, you’ve probably considered a double chain. The chain meshes with the sprockets on either side of the gears. It comes in different styles, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The CZPT duplex series has twice the power capacity of standard SC duplex chains. This type of chain is usually best for new applications. On the other hand, SC double chain chains are the cheapest but have less weight and power capacity.
Another option is a triple drive chain. This type of drive chain has an additional row of plates and contains three sprockets. Its unique design reduces the weight and impact velocity of the timing chain. It is usually used in automotive applications. It is ideal for low to medium-load timing applications. It is also available in acoustically optimized versions. Three-quarter inch pitch double chain chains are widely used in gasoline engine aids and timing drives.
flat top chain
High friction rubber is usually installed on the top or bottom of a flat top drive chain to improve its high friction surface and prevent interference during side bend conveying. The chain plate can be customized with thin rubber layer or thick elastic polyurethane rubber according to customer requirements. In addition to providing high friction, the flat top chain also provides excellent anti-slip properties for glass bottles.
Premium steel flat top chain with high quality surface finish and excellent wear resistance. They have a high level of noise reduction and can be used in heavy duty conveying applications. These chains are available in a variety of alloys such as stainless steel or aluminum. Some models are designed to be very rugged and last longer. Aluminum and galvanized steel chains are popular choices for these chains.
Flat Top Drive Chain Conveyors are versatile and come in an endless combination of configurations. Drives can be connected end-to-end to form long conveyor lines, while side-curved flat-top chains are versatile enough to handle tandem, serpentine or carousel configurations. Standard and heavy duty models are also available. Flat top chains can be used in many different applications including food, beverages and other commodities.
Standard flat top chains are usually rectangular or L-shaped and designed for use on straight conveyors. In some cases, space constraints may require a U-shaped or rectangular conveyor line. For smoother conveying, side-curved flat-top chains can be used. These chains are paired with regular rectangular chain plates and tall pins for high load capacity. They come in different widths, including multi-strand chains.


editor by Cx 2023-06-29
China 10mm 18k Gold Plated Curb Cuban Link Chain Mens Hip Hop Cuban Necklace Spring Buckle Miami Stainless Steel Cuban Chains agricultural roller chain
Model Variety: LT571
Jewellery Major Materials: Stainless steel
Substance Kind: stainless metal
Diamond shape: Round Excellent Cut
Pearl Variety: Other
Gender: Unisex, Women’s, Men’s, Children’s
Major Stone: ZIRCON
Jewelry Variety: NECKLACES
Necklaces Sort: Chains
Celebration: Other, Anniversary, Engagement, Present, Wedding ceremony, Celebration, Other
Chain Sort: Link Chain
Plating: 14K Gold Plated, 24K Gold Plated, Rhodium Plated, 10K Gold Plated, Titanium Plated, 18K Gold Plated, Gold Plated, PVD plated
Shapepattern: cuban
Type: Fashionable
Inlay technological innovation: Micro insert
Key word: cuban link chain necklace bracelet
MOQ: 2pcs
Services: OEM ODM Custom-made Fall Delivery
Size: 10mm,12mm
Substance: stainless steel
Colour: Gold,silver
Transport: UPS DHL EMS Fedex TNT
style: Hip Hop Jewellery
match for: girl, NMRV +NRV Worm Gear Reducer Worm Gearbox males,women,female,gentlemen
Packaging Information: Each solution in 1 opp and far more in a massive opp.
Products Description Packing & Supply To much better make sure the safety of your products, specialist, environmentally welcoming, handy and effective packaging services will be offered. FAQ 1.Q:What can i do prior to area the purchase ?A:Affirm the produce photograph,size,coloration,logo,delivery approach payment strategy,shipping time,declared value,and other customrequest. 2.Q:How to place the purchase ?A:We will send you an bill,little purchase entire payment,big purchase 30% earnest cash to generate,the relaxation payment beforeshipping.when we have stock we will ship in 2-3 days. 3.Q:What can we do after send out the payment ?A:We will hold update and deliver you news when we get from our factory,and keep in contact. 4.Q:I can’ 2571 scorching sale mining equipment portable piston air compressor 15kw utilised with jack hammer t find any news when tracking the track number.A:Most time,we can tracking,sometimes the express company not update the information,let’s hold out 1-2 times a lot more,we will contactexpress,also the monitoring variety have turned new number.6.Q:If there is damaged productsA:We have examine it very carefully ahead of the cargo,but the shipping and delivery providing is uncontrollable,but never ever be concerned about it,get in touch with usin time and get photographs,we will aid heading on this scenario,primarily,we will make discount or refund and use on next get. 7.Q:About the re-buy.A:We will make very same goods and same deal like last time,if there is some adjust,these kinds of as bundle or insert a emblem,permit us knowbefore we make it. PS:Outdoors of work,no make a difference if we have did the company,we are friends,if you have opportunity appear to China, 55567048 55567049 55568386 Camshaft sprocket Timing wheel for Cruze 1.6 1.8 Sonic trax Hideo Epica Aveo Opel Astra Zafira make certain pay a go to ourcompany,I invite you for Chinese tea.

How to choose a roller chain for a conveyor
When choosing a roller chain for your conveyor, the easiest way is to refer to the horsepower and RPM charts. The horsepower and rpm of the small drive sprocket will determine the size and number of teeth of the chain. Conveyor chains are available in a variety of options, including moving products horizontally, vertically, or around a bend radius. When choosing a conveyor chain, consider the purpose of the chain. For example, if you’re delivering products to customers’ doorsteps, you might choose chains that can move products up and down a hallway or warehouse.
Double pitch
Double pitch roller chains are a popular way to drive agricultural equipment. It has twice the pitch of a standard roller chain and is ideal for light-duty drives. Extended pitch increases performance at lower speeds, but requires fewer components per foot than standard single-pitch chains. Compared to single-pitch roller chains, double-pitch chainplates are longer and are suitable for lighter loads. Read on to learn more about double pitch chains and how they can improve your operation.
The most common type of conveyor chain is double pitch. It is used in the auto parts industry, as well as in the precision machinery industry. It is made from the same components as the standard drive roller chain, except it has longer side plates. Double pitch chains are often used on slow-moving conveyors to reduce the stress placed on them. Industries that commonly use double pitch conveyor chains include airport equipment manufacturers, lumber mills, and fruit packing plants.
RS series roller chains are manufactured from high-quality stainless steel. It has excellent chemical and abrasion resistance and is available in a variety of cord lengths. RS sprockets have over 30 teeth. They contain all the necessary connection links for easy installation. PEER Chain offers double pitch roller chain attachments including pre-stretched chains, sprockets, and other attachments.
Double pitch roller chains have several advantages over standard chains. Double pitch chains have double the pitch, making them ideal for conveying applications such as conveyors. In addition to that, it also provides ANSI-compliant styles. These chains also have free connection links. When shopping for a double pitch roller chain, be sure to choose the one that fits your requirements and budget. They will last longer and save you money in the long run.
Double pitch roller chains to ANSI standards feature oversized rollers. These chains are best suited for applications where the product is mounted on top of the chain. They are ideal for agricultural applications where cotton is on top of the drum. Also, this type of chain is used in light-duty conveyors and agricultural applications. You can find double pitch roller chains in a variety of sizes and styles. And, as long as you know what you want, you’ll be happy with the results.
Self-lubricating
Self-lubricating roller chains eliminate the need for manual relubrication, providing long-lasting operation and reducing maintenance costs. These chains are particularly popular in industries such as the food and beverage industry, textiles, printing, and sawmills. They can also replace standard roller chain drives and conveyor chains. Manufactured to the specific standard ISO R606, these chains are ideal replacements for conventional chains. PC chains are particularly beneficial for food and beverage production and packaging applications due to their anti-corrosion properties.
Self-lubricating roller chains meet ISO, ASME/ANSI, and DIN standards. They are interchangeable with standard chains of the same size and shape and can be used in a variety of industrial applications. Self-lubricating chains have special oil-impregnated sleeves to reduce maintenance time. These chains are also suitable for applications where cleanliness is an issue.
Self-lubricating roller chains are manufactured with unique RS attachments. Rather than a traditional roller chain with an external lubricating ring, this type of chain retains the lubricant within its bushings. During operation, the application generates heat, heating the lubricant, which flows out of the pin and bushing area. Therefore, CZPT roller chains are ideal for certain food conveying applications.
In addition to self-lubricating roller chains, carbon steel, stainless steel or nickel-plated steel are also available. Self-lubricating roller chains are available in different sizes depending on the application, including 0.375″ wide profile straight-chain, extended pin chain, and four-link. In addition, these chains are also available in ANSI and BS chain specifications.
Accumulation
Whether you need to move large or small loads, accumulating roller chains are a viable solution. This chain conveyor is designed with low back pressure to transport large and bulky items with minimal noise. Free-running rollers within the chain help create a smooth build-up surface. These chains are available in a variety of options, including accumulating rollers of different pitches.
The accumulation and release roller chain 14 includes an upper part 15 and a lower part 16. The upper part 15 rests in the upper subspace 28, while the lower part 16 rests on the top side 20 of the profile. As the upper belt 15 rolls around the accumulation roller chain 14, it aligns with the lower chain 16 to form a continuous receiving space. This arrangement allows the accumulation roller chain 14 to rest on the top surface of the support profile 11.
A cumulative roller chain consists of many individual parts. Each section of the chain has an elongated cylindrical shape and is connected to each other by hinged joints. Each chain section also has an accumulation and release roller associated therewith. Each roller protrudes from the upper side 20 and the lower side 21 of the chain portion. The accumulation rollers are movable about an axis 22 extending transversely to the longitudinal axis of the chain.
A feature of the stacking and releasing roller chain is its simplicity. The conveyor has a profiled section that is permanently divided into two cross-sectional spaces. The bottom space is closed from all sides. The upper space accommodates the conveyor line. The contoured portion includes an opening that guides the bottom strap. A shunt can also be inserted between the two sections. The accumulating roller chain system is a convenient and versatile way to move bulky items.
There are many different types of accumulating roller chains. Some chains have offset rollers for optimal load distribution. Others have protection to prevent machine wear. Some run without lubricant, which is a safety advantage. In addition to protection, cumulative chains can also provide protection. The side bow version of the accumulation and release roller chain with offset accumulation and release rollers is designed for conveyor systems with very small bend radii.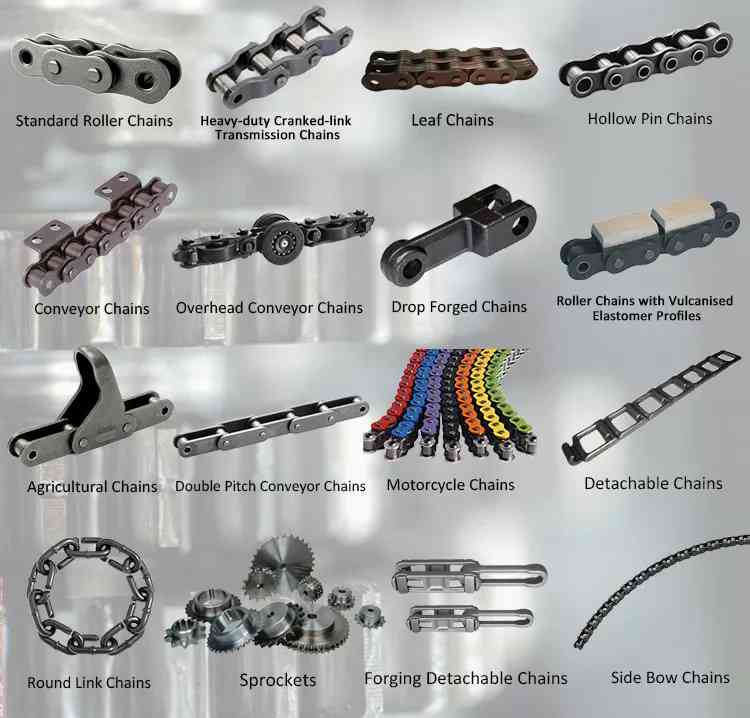
Without bushing
Bushless roller chains are the most common type of industrial chain. They are simple in design and require only regular maintenance. Regular maintenance includes lubricating, assessing wear, and replacing worn sprockets. For more information, please read the following information:
The outer chainplates and the inner chain plates are alternately arranged in pairs. The connecting pin extends through the hole in the inner link plate. The rollers thus positioned can be rotated on the connecting pins. Oil provided between the outer circumferential surfaces of each connecting pin serves to lubricate the chain. This system reduces noise and wears caused by collisions between inner chain plates and sprockets.
Compared to traditional roller chains, bushings roller chains have rollers around the bushing. These rollers are in rolling contact with the sprocket teeth, providing low friction and excellent wear resistance. To ensure smooth operation, bushings roller chains must be greased to prevent rust and keep the chain properly tensioned. Lubricated chains run smoother and last longer.
In a bushingless chain, the inner links are shaped like half bushings and ride on the rollers. The pins go through the outer plate and connect the inner links to the rollers. The outer plates overlap the inner links and open the pins. This system is also known as a heterochain. This type of chain is more common than traditional roller chains. If you are not sure which type of bushingless roller chain to choose, you may need to purchase an additional pair of inner chainplates.
Linerless roller chains may also include chain guides. In a bushingless roller chain, the outer and inner link plates conform to the surfaces of the guide rails. Thus, the large area of contact between the chain and the guide rail is eliminated, the friction loss is reduced, and the power transmission efficiency is improved. These properties make bushless roller chains more efficient and durable than traditional roller chains. It’s also less noisy. If you are looking for a chain with a lower noise level, a bushingless roller chain may be the right choice for you.


editor by Cx 2023-06-28
China high quality Lf882tab-K750 190.5mm Flexible Conveyor Top Chains Sideflexing Chains blind roller chain
Product Description
| The 880 series has a wide range of applications for conveying lightweight items in curves e.g. plastic bottles, cans, cartons etc. This space-saving chain is often used with small diameter turn discs with ball bearings. Plate mat.:POM/PP; Pin mat.:stainless steel Max.speed: 80m/min lubrication; 50m/min dry;Max.length:15m; Working load:2680N Color:white/brown; Packing unit:10ft(80links) |
| APPLICATIONS: |
| China CZPT Machinery Co.,Ltd is a special supplier of conveyor system components,including plastic and stainless steel flat top chains, Modular belts, other spare parts, such as UHMWPE wearstrips, side guards, chains guide, bipods, tripods, brackets, clampls.ect. With our years of experence, quality products, excellent services we work with world wide clients from America, Europe, Africa, many counrties of Asia. We keep very good business relation with them, and get trusted from them. Our products application: Packaging and conveying industry |
| Material: | Plastic |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Top Chain |
| Surface Treatment: | Low Friction |
| Chain Size: | Pitch 38.1mm |
| Color: | Brown/White/Others |
| Materials: | POM/PP/PE |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Roller Chain Maintenance Tips
There are many things to keep in mind when maintaining a roller chain. The main reasons include friction and external influences. Without proper lubrication and adjustment, such chains will wear prematurely. Here are some tips for keeping your roller chain in top shape. continue reading! This will make your process easier. We will also discuss the cost of the new roller chain. As always, remember to check for loose ends and adjust the chain regularly.
Preloading
Roller chains are designed to accommodate many different types of loads. Sprockets are the main cause of chain wear. Axial and angular misalignment occurs when the sprocket faces are not properly aligned. Both types of misalignment increase stress and wear on the roller chain. They can also negatively affect the drive. Therefore, choosing the right chain is an important consideration.
Preloading helps to eliminate initial elongation and extend service life. The benefits of preloading can be seen in the preloading chart. Significant elongation occurs during drive startup with no or minimal preload. This is due to the surface hardness of the worn parts. On the other hand, a properly preloaded chain shows little elongation during the initial start. Therefore, proper preload can prolong wear life.
Although elongation is a natural phenomenon in any drive, it can be minimized or eliminated with proper maintenance. In addition to regular inspections, you should do a full inspection of your chain after the first hundred hours. This inspection should focus on key life factors such as 3% elongation, how the chain is lubricated, and any other issues that may affect life. A good quality chain should have the longest life and no problems.
There are many different roller chain specifications. A good rule of thumb is to choose chains with at least five links. Then, tighten the chain until a break occurs, and it will tell you what kind of break occurred. Alternatively, you can use a roller chain with the maximum allowable load. As long as the MAL doesn’t exceed that number, it’s still perfectly safe to use it for any application.
lubricating
When it comes to lubrication, there are several different techniques. For example, spray lubrication is a popular method for high-horsepower drives and high-load and fast-moving machines. This method is very effective, but it is expensive, and spraying the chain too far out of the guard can cause leaks. Another common method is brush lubrication. Brush lubrication involves applying a continuous flow of oil to the chain, pushing it into the chain. This lubrication technique reduces the application temperature of the chain. Also, it can extend the life of the chain, depending on the manufacturer’s specifications.
While the lubrication of roller chain couplings varies by application, sprocket hubs should be lubricated monthly to ensure proper sealing. The amount of oil used depends on the rotational speed and the type of roller chain coupling. In general, lubricants used in roller chain couplings should have excellent adhesion, oxidation, and mechanical stability.
Wear-resistant lubricants are recommended. They prevent the rollers from sticking to each other and prevent rusting. These lubricants have low surface tension and are not harmful to metal or O-ring chains. The optimum lubrication method depends on ambient temperature, horsepower, and chain speed. Properly lubricating a roller chain increases the life of the chain and reduces the risk of wear.
Proper lubrication of the roller chain is essential to prevent corrosion and prolong its service life. The oil forms a smooth film on the chain components, reducing metal-to-metal contact and minimizing friction and wear. Additionally, the oil provides a smooth running surface and reduces noise. However, the running-in process of roller chain lubrication cannot be underestimated. When using heavy-duty oils, ensure that the lubricant is compatible with operating and ambient temperatures.
Maintain
To extend the life of your roller chain, you need to carry out regular inspections. First, you should check the T-pin on the link plate at the joint. If they are not connected properly, it can cause the chain to stretch and not maintain proper spacing and timing. Next, you should look for unusual noise, corrosion, and dirt that may indicate wear. If you notice any of these problems, it’s time to replace the chain.
In order to properly maintain a roller chain, both areas of the roller chain must be lubricated with the correct lubricant. Lubricants used should be SAE non-degreased oils. There are several types of lubricants available, but the best one is a petroleum-based oil with a high viscosity. You can also check for signs of wear, such as red or brown discoloration. This means that there is not enough lubrication.
While the life expectancy of a roller chain is unknown, it is important to know how to extend its life and maximize its effectiveness. Improper tension and alignment can shorten its life and place undue stress on the drive system and the chain itself. Incorrect tension can also lead to slippage and increased energy output. Therefore, you should calculate the tension and alignment of the chain during the initial installation. Check and adjust regularly.
Another way to extend the life of your rollers is to thoroughly clean the inside and outside of the rollers. You should also lubricate it frequently to prevent excessive heat buildup. Designed to prevent overheating by limiting the amount of work during break-ins. Additionally, regular inspections will help you catch anomalies early enough to stop operations. Last but not least, regular lubrication will prolong the life of the roller chain.
Cost
Buying a roller chain is a big decision, but initial cost shouldn’t be the only consideration. The cost of the roller chain itself, as well as the running costs, should be considered. Even the lowest-priced chains can be more expensive in the long run. Additionally, maintenance and energy costs may increase. The best roller chain for your business will be the one that best suits your needs. Listed below are some considerations to consider when purchasing a roller chain.
First, what material should you use? Roller chains come in many different materials. Stainless steel is a commonly used material in construction. Materials are selected based on the cost and design of chain horsepower transmission. Various manufacturing processes will determine which material is suitable for your application. Also, the weight of the chain will vary depending on its pitch and the construction technique used. A large part of the cost of a roller chain is on the drive sprocket.
Another consideration is installation cost. Roller chains are commonly used in agricultural and transportation applications, especially for agronomic products. If lubrication is your concern, maintenance-free chains are the best choice. Corrosion-resistant chains are ideal for wet environments. They are sold in boxed lengths, so replacing a longer length requires adding a shorter length. To avoid trouble, use the skateboard to help connect the links.
Another consideration is the overall width. The overall width of an open #40 roller chain may vary but should be at least 10 feet wide. Although it is not the most expensive type of roller chain, it will last longer. Using it correctly will increase its overall longevity, so it’s a good idea to choose it wisely. If your business uses roller chains regularly, the cost reduction is well worth it.
Application
A roller chain consists of a pair of alternating pins and roller links. The pins are pressed into the side panels and hinged to the rollers. Roller chains can be single or multi-strand, connected by a common pin. The multi-strand design provides higher shear strength for demanding power transmission applications. Typical applications for roller chains include conveyors, hoists, and other mechanical equipment.
The horsepower capability of a roller chain is limited by several factors, including pin shock and friction. While research into these factors has placed some limits on the maximum operating speed of the roller chain, practical experience has shown that these systems can be used at higher speeds. Proper lubrication and cooling can increase the durability of these chains. In addition, roller chain applications include:
Drive and conveyor systems are the two main uses of roller chains. During driving operations, wear and elongation are a natural part of the operation. However, lubrication plays a vital role in minimizing wear and shock loads. Therefore, wear is inevitable and special care must be taken to ensure proper lubrication. Additionally, lubrication reduces heat dissipation in the chain.
The materials used to make roller chains vary from one type to another. Stainless steel is common, but nylon or brass are sometimes used. These materials are less expensive and more durable than steel or stainless steel. The best material for the job depends on a variety of factors, including cost, environmental conditions, and design horsepower transmission. For example, the pin bushing contact area is a critical area requiring lubrication. Additionally, some coatings are designed to retard the corrosive effects of water or oil.

editor by CX 2023-06-12
China supplier Car Chains Snow Chains Tire Chains bush roller chain
Product Description
CZPT tire chains pattern in sures a comfortable drive with less vibration and noise,
Masimum traction with ninimal brake distance and skidding,
The small square links and the short length of each cross chain minimizes wear and breakage,
Easily operated chain tensioning system,
Fitted in minutes,wthout the need to jack up,or move the car,
Unique “D” type square link design,gaining excellent traction,
Flexible steel cable covered with plastic sheath,
Thermal treated electro-galvanised chains,
Elegant and strong plastic case,safe and convenient,spacesaving,
Comes complete with installation instructions,repair links 1 pair/case.
| After-sales Service: | Replacement, Credit |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Material: | Steel |
| Usage: | Car Chains |
| Manufacturing Process: | Weld Chain |
| Transport Package: | Crate |
| Samples: |
US$ 25/Pair
1 Pair(Min.Order) | |
|---|
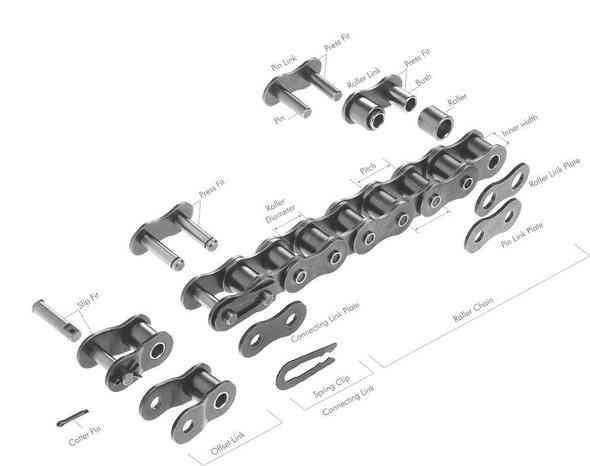
What to look for in a roller chain
There are many different factors to consider when purchasing a roller chain. One of the most important factors is tensile strength, which represents the force required to break the chain. Roller chains are available in three different tensile strengths: minimum, average and ultimate. Each strength reflects a different limit to the load the chain can handle. However, these limits are not always equal and you should be aware of the differences between roller chains.
Canonical chain
Most roller chains have standard sizes printed on the side panels. This is usually “40” or “C2080H”, but can also be the letter “B”. If the chain is old, it will need to be cleaned to see its size. You can find the size on the standard roller chain size chart, but not everyone is marked. To determine the size, measure the diameter and pitch of the chain, then compare the results to the chart to see what size you need.
Heavy-duty roller chains are available with heat-treated pins, side plates, and rollers. In addition to being heat treated, they are also factory pre-stretched, which reduces wear on these parts. If properly maintained, they can last for years, reducing the risk of failure or corrosion. Depending on the application, standard roller chains are available in different sizes. It can be purchased separately. There are several options to choose from, depending on the size and strength of the application.
PEER roller chains contain solid rollers to reduce shock loads on the sprocket teeth. Heat treating and preloading all components of the PEER chain helps minimize initial elongation. Hot-dip lubrication ensures complete lubrication of all chain components, extending their life and reducing maintenance costs. For heavy-duty applications, ASME/ANSI-B29.1 chain is a good choice.
Standard roller chains are made of steel or alloy steel. However, it can be made of other materials such as stainless steel. In addition to steel, stainless steel is often used in food processing machinery where chain lubrication is an issue. Brass and nylon are also sometimes used. However, they are not that popular. Therefore, you should always check with your supplier before purchasing. By comparing the tensile strength of two different chains and making an informed decision, you can get the best price and service.
Chain without bushing
Bushless roller chains have advantages over conventional roller chains. Unlike conventional chains, bushless chains have extensive lateral flexibility, which increases the chain’s lubrication flow. The inner plates of bushless chains have protruding shoulders so the oil can flow through them more easily and efficiently. This is an important characteristic of a smooth-running chain. Additionally, bushless chains may have improved shifting performance.
The strength of a bushingless roller chain is measured in terms of tensile strength and fatigue strength. The former measures the load a chain can withstand before breaking. Fatigue strength is equally important, and factors that affect fatigue strength include the steel used to make the chain components, the pitch hole fabrication, the type of shot peening on the chain, and the design and thickness of the chain. For example, if the chain is too thin, it may not be enough for heavy-duty applications.
Like traditional roller chains, bushingless roller chains have two different types of links. The inner link has two inner plates connected by pins, while the outer chain has two outer plates held together by bushings. A bushingless roller chain is similar to a traditional chain, except it eliminates a step in the assembly process by stamping the tube into the inner plate. So if you want a smoother ride, a bushingless roller chain is a better choice.
There are two different sizes of bushingless roller chains. One size is designed for use with standard single-strand chains, while the other size is designed for use with double-strand or triple-strand chains. Bushless chains are generally shorter than conventional chains, so they can fit in tighter spaces. Bushless chains are made of the highest quality materials. These chain attachments are case hardened for optimum strength and durability.
Mute chain
The silent roller chain has a smooth, low-noise drive. They are made of stacked rows of flat chainplates with a gear-like profile that meshes with the sprocket teeth. Each chainplate is attached to a corresponding sprocket, which also allows the chain to bend. While these basic components are the same for every silent roller chain, there are many variations that allow them to be used in a variety of applications.
The most popular high-speed transmission, silent chains feature gear-like sprockets. They can be made from single or multiple strands of material. Single-strand chains are less expensive than multi-strand chains, but they tend to wear out faster if not lubricated. Single-strand roller chains can be used for years without lubrication, but for your application, wide silent chains are still worth considering.
The design and construction of silent chains make them ideal for conveying a wide variety of products. They have flat, heat-resistant surfaces. They are also durable and non-slip. They are available in a variety of pitch sizes, widths, and mounting styles. Whether you need chains for general purpose conveyors or glass bottle transport applications, we have you covered. Ask about the benefits of silent roller chain conveyors.
Inverted tooth chains are another option for quieter chains. These chains are designed to reduce noise from engine-related friction. Silent chains are more common, and manufacturers have fallen in love with them. A silent chain consists of several links connected to the sprocket teeth. Teeth rotate to reduce noise, vibration, and chord action. These are the main reasons why silent chains are so popular.
ANSI chain pitch
To measure your bike’s chain pitch, you can use a caliper. This measurement is taken from the center of the rolling pin to the center of the next rolling pin. Chains come in many sizes, but ANSI is the most common chain standard in the United States. A caliper is handy if you’re not sure which size to buy, as it allows you to check for worn sprockets.
Chains that meet ANSI standards will be characterized by a certain pitch. This measurement is based on the width and spacing of the roll. The spacing is usually greater than the width. The standard number will be the right number for the width of the chain or the left number for the rollers. The number on the left indicates whether the chain is lightweight or heavyweight. Heavyweight chains are designated by the suffix “H”.
Common chain sizes are based on ANSI chain pitch. Pitch is the minimum distance between bushing and sprocket. The smaller the chain pitch, the greater the total distance between the two points. This means the chain will last longer. However, if you are buying a chain for a specific application, you should check the pitch carefully as it can affect the performance of the chain.
Roller chain wear measurement
The purpose of roller chain wear measurement is to prevent breakage by monitoring the strain on the chain. There are several ways to measure roller chain wear. The first is to remove the chain from its working position and measure the distance from the sprocket to its measuring end. Another way is to measure the pitch of the chain or the distance between two pins. This method is superior to other methods because it is convenient and accurate.
When measuring the wear of a roller chain, it is important to note that the elements of the chain will gradually deform. About 3.75% of the total wear will be on the pins and the rest will be on the internal links. These wear measurements will vary based on the nominal pitch of the chain and the amount of friction the chain is experiencing. Proper lubrication between pins and bushings, load and frequency of articulation all affect wear rates.
It is important to measure the amount of wear on the roller chain to avoid excessive machine failures. The longer the chain runs, the more wear it will wear. Although the length of the chain should be less than the center distance, the excessive load will cause premature wear. Therefore, lubrication is essential. Additionally, the sag of the chain should not exceed 2% to 4% of its center-to-center distance. Finally, check for unusual noise or visible defects. A common cause of excessive roller chain wear is the size of the load. Every chain manufacturer sets a maximum workload for its product.
There are several ways to measure roller chain wear. If using a high-speed drive, it should have at least 11 teeth, and a medium-speed drive should have at least 25 teeth. Also, be sure to check the length of the chain, even if you should. The same goes for the pin diameter, which should be the same or different pitch as the roller chain.


editor by CX 2023-06-09
China 2021 Africa Bangle Thick Cuff 18K 14K Gold Plated Chains Women Bracelet Bangles Ladies Set For Women roller chain conveyor
Error:获取session失败,

Roller Chain Basics
Before choosing the right roller chain for your machine, it is necessary to learn some basics. Learn about sprockets, tensile strength, pitch, and width. Read this article to learn more. It will help you make an informed decision. Getting the right product is critical, but it’s not always as simple as choosing a brand name. You need to choose a company that supports its products and provides good service.
Roller sprocket
If you are planning to purchase roller sprockets for your application, you should first look at the various types available. Sprockets available for single-strand roller chains are manufactured by Boston Steel – Type B sprockets are drilled to size. They are available in 1/4, 3/8, 1/2, 5/8, 3/4 and 1″ pitch sizes.
The diameter of the sprocket is important when choosing the right sprocket for your application. Using a caliper to measure the diameter of a toothless plate is a good way to determine the exact size of the sprocket. A caliper is the diameter of a plate without teeth. On Type B and C sprockets, the hub diameter measures the thickness of the hub.
Another type of sprocket is the steel split sprocket, which is split in diameter. This type is easy to install and remove, and is held together by bolts in the hub. Typically, split sprockets have chain pitches ranging from 40 to 240 and bores ranging from 3/4″ to 6″. The split sprockets are designed with one pointing towards the ceiling and the other two parallel to the floor.
When shopping for sprockets, it is important to remember that they are designed specifically for a specific chain. All chains are manufactured to specific standards. In the United States, the most common standard is ANSI. The chain pitch is the distance between the center of each pin and the center of the next pin. In the US, the standard is always measured in eight-inch intervals.
In addition to sprocket size, sprocket pitch and the surface area also affect chain life. Unlike belt sprockets, which are made of forged steel, the teeth on roller sprockets are stamped from steel sheet or pressed from powdered metal. The harder the teeth, the longer the chain will last.
Roller chain pitch
The pitch of a roller chain is the distance between the sprocket and the pin. The smaller the thread pitch, the smaller the bushing wear. Generally speaking, the smaller the pitch, the longer the life of the chain. For best performance and longest life, manufacturers recommend a minimum chain pitch of 2% to 3%. Chain pitch is important to ensure proper performance, and the manufacturer recommends that you replace the chain when it reaches 2% to 3% of normal.
To determine the correct chain pitch for a particular chain, first determine the sprocket size and pitch. Pitch is the distance between pin centers, measured in 1/8 inch increments. The pin diameter of the chain is also important. If you’re not sure about the pin diameter of your chain, measure a few links to get a good average reading. Alternatively, use a caliper to measure the inside diameter of the sprocket and count the number of teeth.
When sizing a sprocket, measure the chain between the gears with a caliper and compare it to the measurements on the chain size chart. Make sure you have checked all the specs and checked the correct chain pitch. Then, choose the correct chain pitch for your needs. This is a critical step in choosing the right chain. So get the correct pitch for your roller chain. Correct pitch helps ensure maximum performance and safety.
To identify a specific type of roller chain, measure its tensile strength. This represents the amount of load the chain can withstand before breaking. Another key parameter to consider is fatigue strength. Chains with high fatigue strength are more resistant to rust and wear than chains with low fatigue strength. The numbers on the right in the standard numbering represent normal or light duty chains, while the numbers on the left represent the pitch of heavy-duty chains.
Double pitch roller chains are a variant of single pitch chains. They are manufactured according to ISO 606 and meet the same standards as single pitch chains. They are mainly used in applications with lower requirements for speed and power transmission. The plates of double pitch roller chains are also longer than single pitch chains. The double pitch drive series is also used for elevator and long conveyor drives. There are three main types of roller chains: single-pitch chains, double-pitch carriers, and oversized rollers.
Roller chain width
When buying a roller chain, one of the first decisions you must make is its width. To make this determination, you need to measure the overall width of the chain, the diameter, and the width of each roller. You must also know the height and thickness of the board. After taking these measurements, you can start shopping for the perfect roller chain. But before you buy a new chain, it’s important to know what to expect from the chain itself.
There are many different types of roller chains. These chains are available for ANSI and metric measurements. They come in single-stranded and double-stranded variants. They are usually used for power transmission. Other types include agricultural, automotive, conveyor, multi-strand, and four-strand chains. These charts also include a chart so you can easily see the exact size you need. Listed below are some of the benefits of buying a roller chain.
Roller diameter and pin diameter are important factors in choosing the correct chain width. The width of the chain is the nearest binary fraction of 5/8 of an inch. It should be at least half the thickness of the sprocket, and the plate thickness is one-eighth the width of the chain. Overweight chains are indicated with the suffix H. The pitch and width of the chain are determined by the working load and machine speed.
The outer links of the roller chain are called pin links. These pins are inserted into the bushings of the adjacent roller links. They are held in place by cotter pins. Pin links are usually pressed into the pins of heavy-duty chains. These pins are used to hold the rollers in place. However, these pin chains can reduce the power rating of roller chains by up to 20%.
The ANSI 29.1 Steel Chain Specification specifies a minimum pitch in inches and ultimate strength of 12,500 x pitch in inches. At the same time, the O-ring chain greatly reduces wear due to its lubricating effect. O-ring and X-ring chains contain a lubricant injected by vacuum when riveting the chain together. Transmission chains are tested and governed by standards bodies such as ANSI. In 2011, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers developed a standard for precision power transmission chains.
Roller chain tensile strength
One of the most important indicators of roller chain strength is tensile strength. This measurement refers to the amount of load the chain can withstand before breaking. Another measure, called fatigue strength, refers to the maximum load a chain can withstand before it breaks. The strength of a roller chain depends on its size, the quality of the steel used in its construction, and the heat treatment. There are also differences in the types of shot peening used to treat steel, pitch holes, and link plates.
When choosing a roller chain, the workload is critical. This is the maximum load the chain can withstand before fatigue failure occurs. This measurement is critical because it helps determine the type of load applied to the chain. When deciding which roller chain to buy, be sure to consider the mechanical type and desired strength. Then, make sure it meets strength and load-carrying capacity requirements.
The ultimate tensile strength of a roller chain is based on the manufacturer’s recommended maximum tensile strength. However, the actual tensile strength may be higher or lower than this value. The working load limit of a roller chain can also be calculated by multiplying the chain diameter by the grade. The working load limit of a chain is the highest tension it can withstand before breaking. This value is usually expressed in points.
The maximum tensile strength of roller chains varies by chain type. The single-strand heavy chain has thick side plates for higher shock loads. Single strand heavy-duty roller chains, also known as “bushing” roller chains, are also available. Double-stranded heavy chains are structurally similar, but they have two layers of steel connected by pins that are nearly twice as strong as standard roller chains.
The tensile strength of a single-strand roller chain is approximately 500 tons. In comparison, a single-chain blockchain has a tensile strength of 900. The tensile strength of the two is similar, and it is not recommended to choose one or the other. Although steel and titanium chains are considered the strongest materials for roller chains, these materials are not magnetic.


editor by Cx 2023-04-26